PRECISION MEASURING AND GAGING - OD1642 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
and convex (outside curve) radii in almost all of the common sizes.
(7) Straightedges.
(a) General. Straightedges look very much like rules, except that
they are not graduated. They are used primarily for checking surfaces for
straightness; however, they can also be used as guides for drawing or
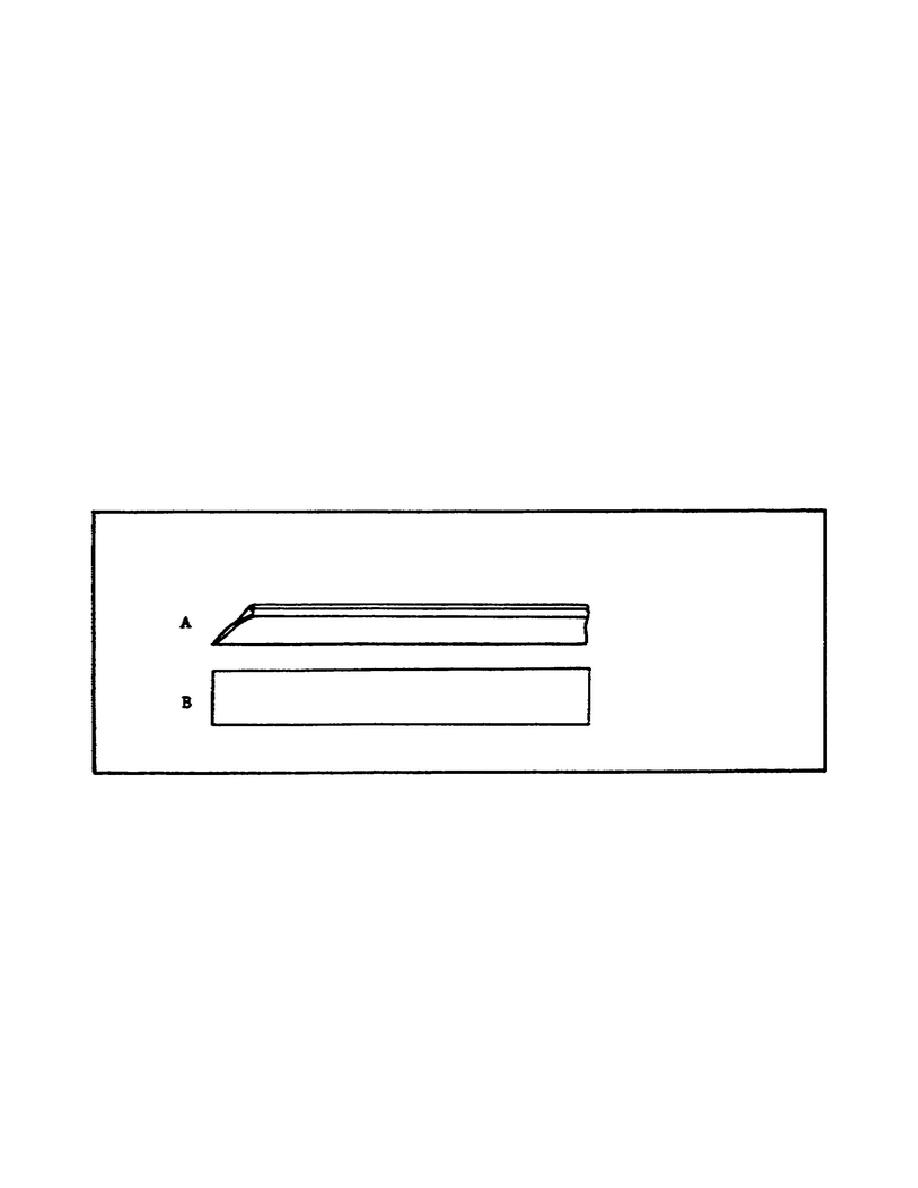
scribing straight lines. Two types of straightedges are shown in figure 23.
View A shows a straightedge made of steel which is hardened on the edges to
prevent wear; it is the one the machinist will probably use the most. The
straightedge shown in View B has a knife edge and is used for work requiring
extreme accuracy.
(b) Care. The straightedges should always be kept in a box when
they are not in use.
Some straightedges are marked with two arrows, one
near each end, which indicate the balance points.
When a box is not
provided, place the resting pads on a flat surface in a storage area where
no damage to the straightedge will occur from other tools.
Place the
straightedge so that the two balance points set on the resting pads.
FIGURE 23.
STRAIGHTEDGES.
(8) Machinist's Square. The most common type of machinist's square
is a hardened steel blade securely attached to a beam. The steel blade is
not graduated. This instrument is very useful in checking right angles and
in setting up work on shapers, milling machines, and drilling machines. The
size of the machinist's squares range from 1 1/2 to 36 inches in blade
length. The same care should be taken with them as with micrometers.
35




 Previous Page
Previous Page
