2. Rectifiers. The purpose of most power supply units is to convert
some AC input to the desired DC output(s) in order to operate the
circuits supplied.
In figure 1-41 you can see that this conversion
takes place in the element labeled as the rectifier.
Rectification
may be half-wave or full-wave.
Figure 1-41A illustrates the
schematic for a simple half-wave rectifier and its resultant
Figure 1-41B shows a full-wave rectifier diagram and
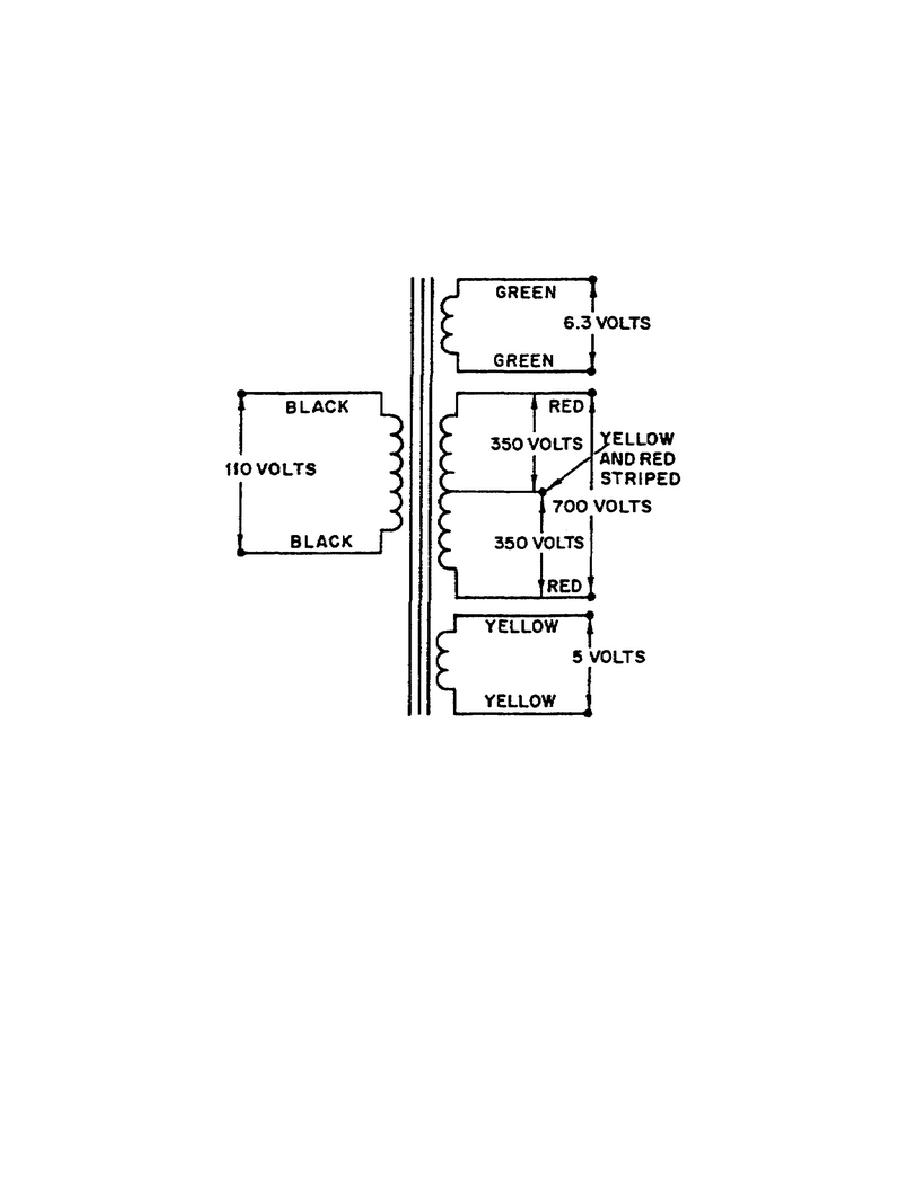
Figure 1-40.
The component common to almost all types of rectifiers is the diode.
The diode may be a vacuum tube diode or a solid-state diode. Since a
diode has the property of passing current in only one direction, it
is ideally suited for converting AC to DC.
In half-wave
rectification, only one direction of current flow is used. In full-
wave rectification, the diodes are so connected as to make use of the
AC current in both directions, thus resulting in the waveforms shown
in figure 1-41.
Solid-state diodes are used in almost all modern
applications.
25
OD1725




 Previous Page
Previous Page
