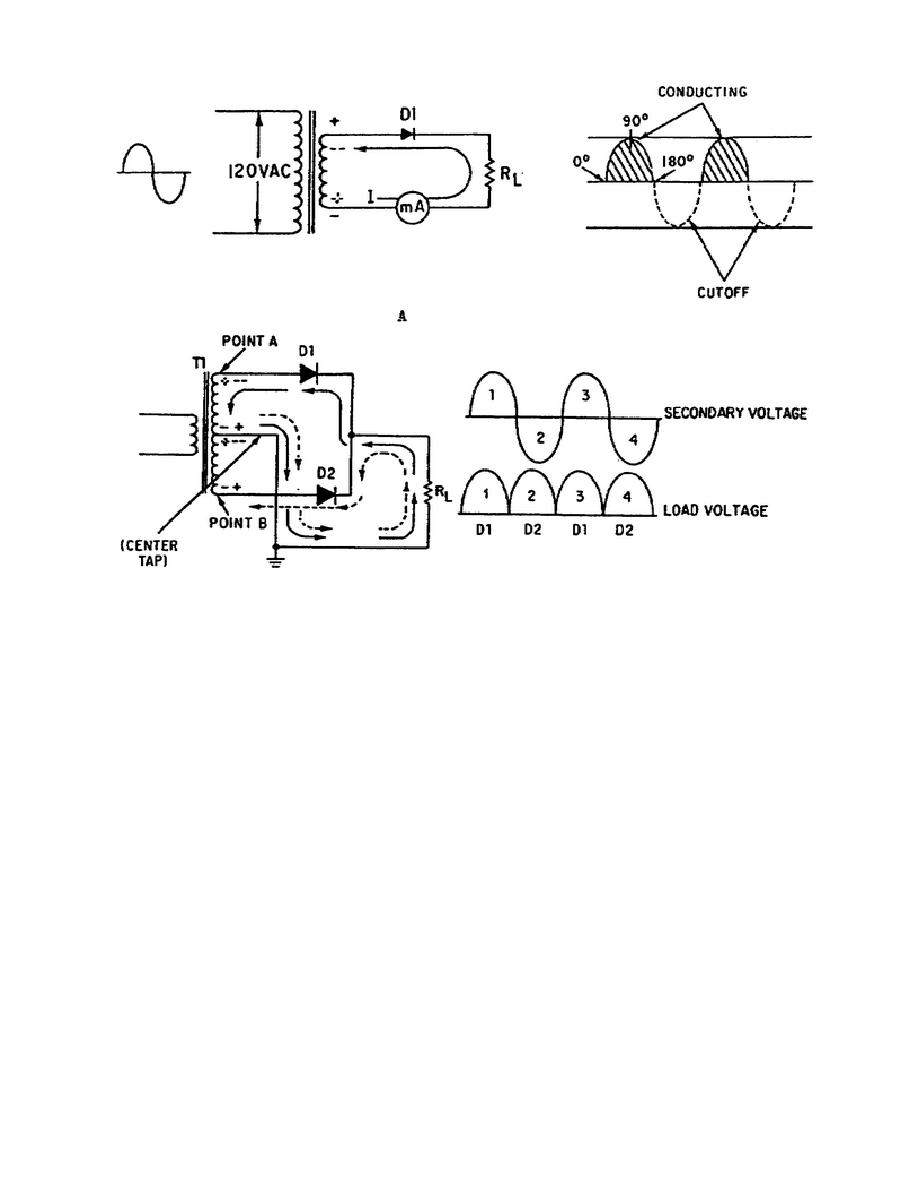
Figure 1-41.
Rectifier Circuits.
3. Regulators. The forth element of the power supply unit shown in
figure 1-42 is the regulator.
The purpose of the regulator is to
provide an output voltage with little or no variation.
Regulators
sense changes in output and compensate for the changes.
Regulators
may also be designed to regulate the current flow.
Voltage
regulators may be classified as series or shunt (parallel), depending
on their relative location in the circuit.
Figures 1-42A and 1-42B
show a shunt regulator and a series regulator respectively. In most
modern practical applications, solid-state devices are used in
regulator circuits.
Figures 1-42C and 1-42D show shunt and series
regulators employing solid-state components.
Zener diodes are used
extensively in regulator circuits.
A zener diode blocks current
until a specified voltage is applied.
When the zener voltage is
reached, the zener diode conducts, thus regulating the voltage
developed across it.
4.
Transistors.
Probably no single event has had the impact on
electronics as has the discovery of the transistor. Transistors have
virtually
replaced
vacuum
tubes
in
most
modern
electronic
applications.
Additionally, transistors have been designed to
perform functions not previously attainable with vacuum tubes.
26
OD1725




 Previous Page
Previous Page
