BASIC ELECTRONICS - OD1633 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
To redraw any circuit, start at the source, and trace the path of current
flow through the circuit.
At the junctions (points where the current
divides), parallel branches begin.
These junctions are key points of
reference in any circuit and should be labeled as you find them. The wires
in circuit schematics are assumed to have no resistance, and there is no
voltage drop along any wire. This means that any unbroken wire is at the
same voltage all along its length, until it is interrupted by a resistor,
battery, or some other circuit component.
In redrawing a circuit, a wire
can be "stretched" or "shrunk" as much as you like without changing any
electrical characteristics of the circuit.
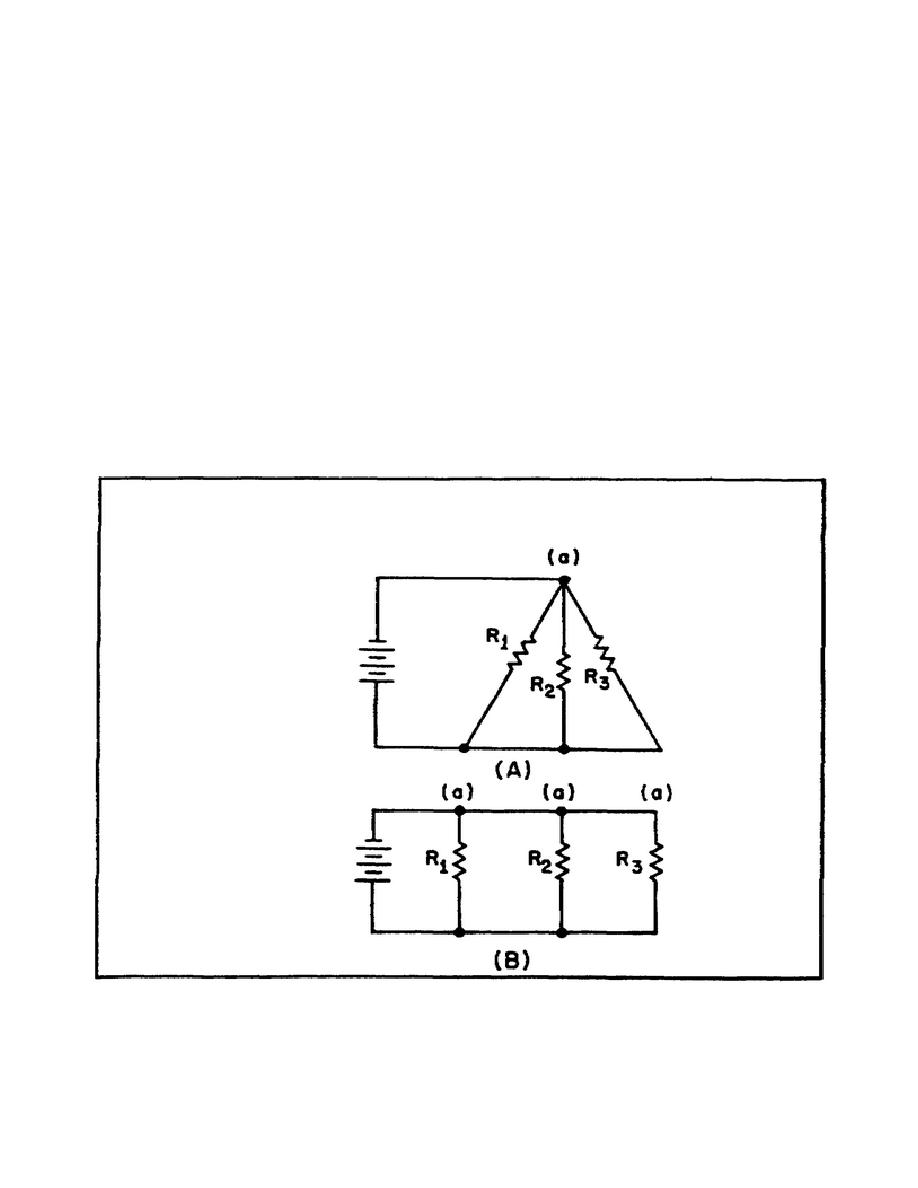
Figure 55, view A, is a schematic of a circuit that is not drawn in the box-
like fashion that was used in previous illustrations.
To redraw this
circuit, start at the voltage source and trace the path for current to the
junction marked (a). At the junction, the current divides into three paths.
If you were to stretch the wire to show the three current paths, the circuit
would appear as shown in view B.
FIGURE 55.
REDRAWING A SIMPLE PARALLEL CIRCUIT.
90




 Previous Page
Previous Page
