MILLING MACHINE OPERATIONS - OD1644 - LESSON 1/TASK 1
(8)
which cannot be obtained by simple indexing with the index plates regularly
supplied. To obtain these divisions a differential index head is used. The
index crank is connected to the wormshaft by a train of gears instead of by
a direct coupling and with simple indexing.
The selection of these gears
involves calculations similar to those used in calculating change gear ratio
for cutting threads on a lathe.
(9)
Angular Indexing.
(a)
When you must divide work into degrees or fractions of degrees by
plain indexing, remember that one turn of the index crank will rotate a
point on the circumference of the work 1/40 of a revolution.
Since there
are 360 in a circle, one turn of the index crank will revolve the
circumference of the work 1/40 of 360, or 9. Hence, in using the index
plate and fractional parts of a turn, 2 holes in a 18-hole circle equals 10,
1 hole in a 27-hole circle equals 2/3, 3 holes in a 54-hole circle equals
1/3. To determine the number of turns, and parts of a turn of the index
crank for a desired number of degrees, divide the number of degrees by 9.
The quotient will represent the number of complete turns and fractions of a
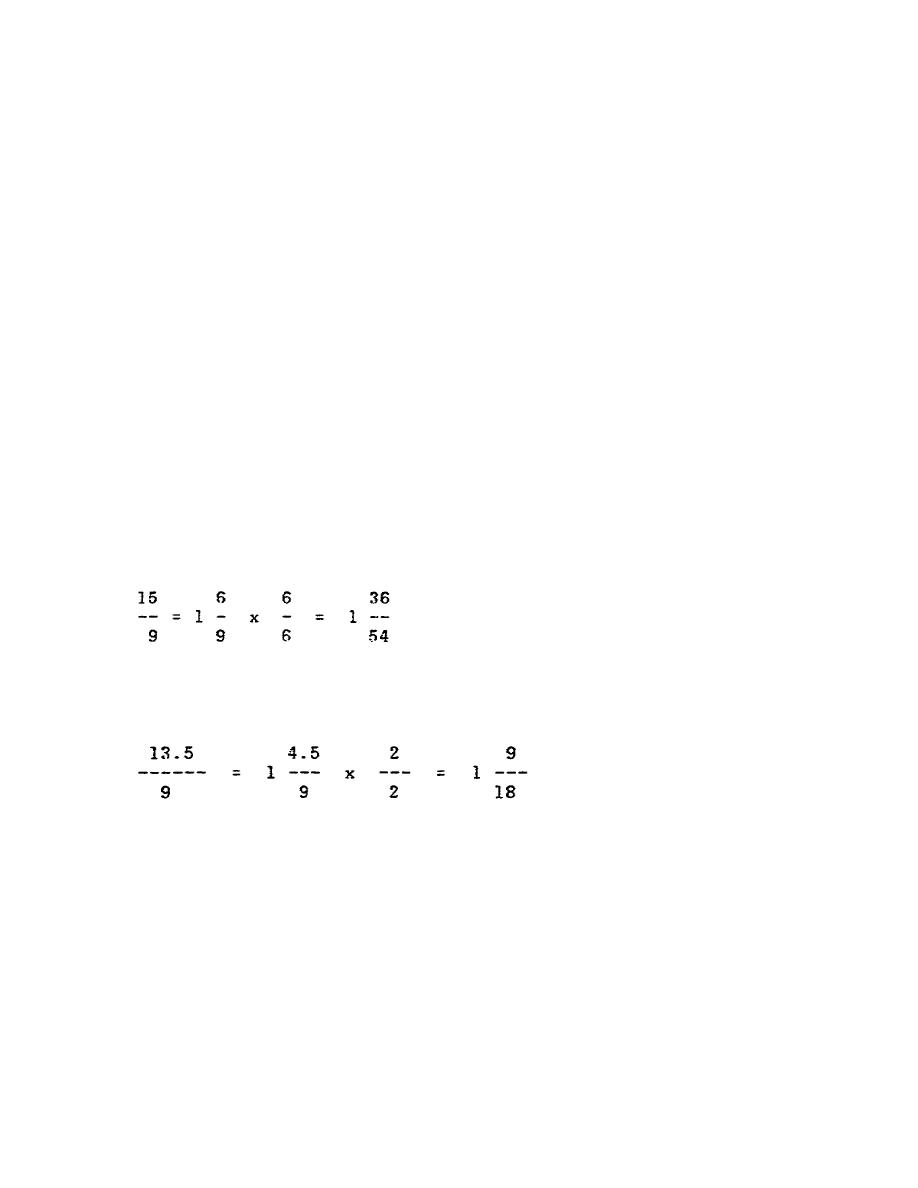
turn that you should rotate the index crank. For example, the calculation
for determining 15 when an index plate with a 54-hole circle is available,
is as follows:
or one complete turn plus 36 holes on the 54-hole circle. The calculation
for determining 13 1/2 when an index plate with an 18-hole circle is
available, is as follows:
(b)
When indexing angles are given in minutes and approximate divisions
are acceptable, movement of the index crank and the proper index plate may
be determined by the following calculations:
26




 Previous Page
Previous Page
