connected battery source, the voltage output of the individual
batteries is additive.
Sometimes series connected batteries are
illustrated the same way as multicell batteries. If the battery has
the proper voltage rating, but lacks sufficient power for the given
circuit, batteries may be parallel connected.
Figure 1-11D shows a
parallel connected battery power source.
The output voltage of the
battery power source is generally indicated on the schematic diagram.
b. Generators.
Another common source of power for electrically
powered equipment is the generator.
Simply put, generators convert
mechanical energy to electrical energy. Depending on the design and
construction of the generator, the output may be set to meet the
needs of the equipment supplied.
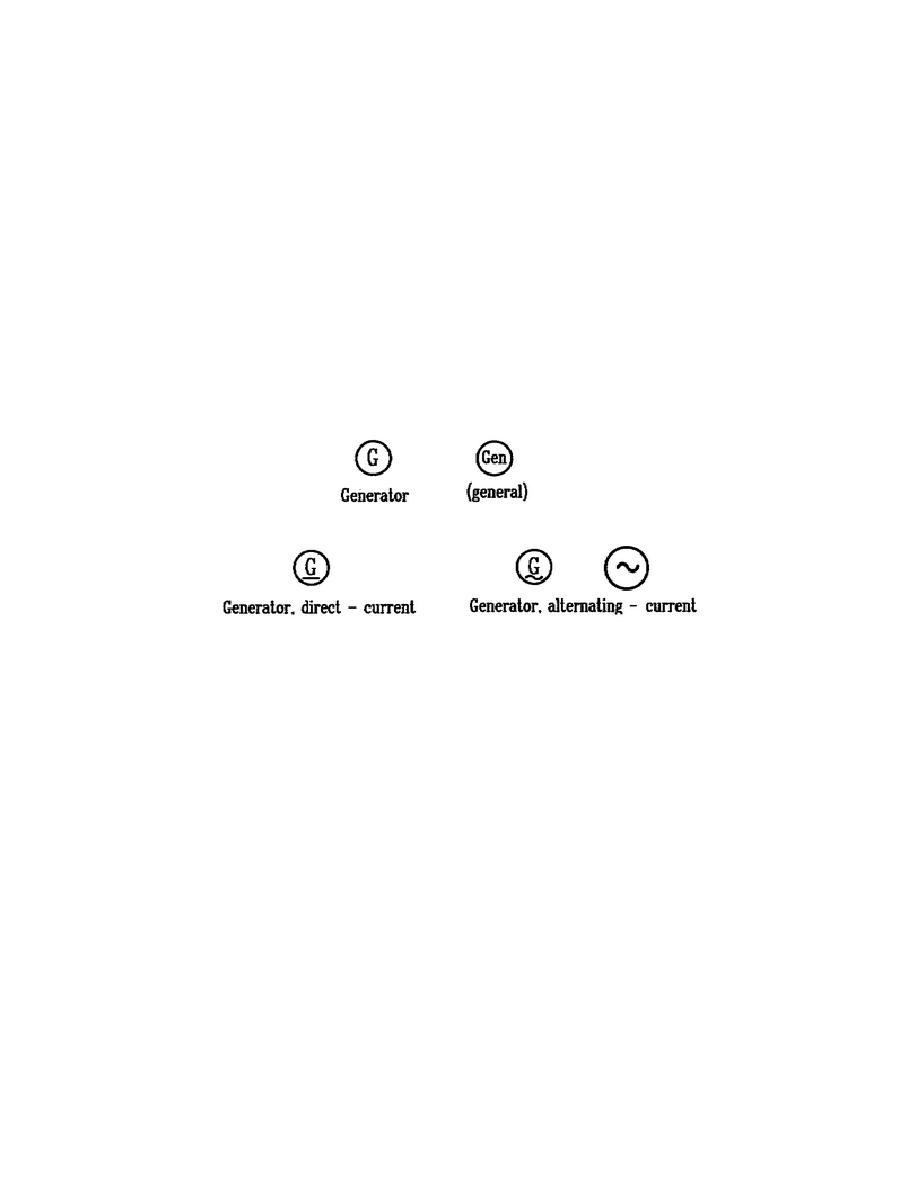
Generators may be designed to
provide either AC or DC power.
AC generators are often referred to
as alternators.
Figure 1-12 shows the standard symbols used to
represent generators or alternators in schematics.
Figure 1-12.
Generators.
c. Transformers.
Although transformers are not a true power
source, they are often the source of the voltages used in a given
circuit.
Typically, an external power source is applied to a
transformer, which converts the input power to the voltage(s)
necessary to operate the circuit supplied.
Transformers are a
special application of inductors, thus the similarity in the
schematic symbol used.
Figure 1-13 illustrates several types of
transformers used in a variety of circuits.
Basically, transformers are two inductors placed in close physical
proximity.
The external input AC voltage is applied to the first
inductor (the primary).
The resulting electrical field will be
"induced"
onto
the
secondary
inductor
(the
secondary),
thus
transferring the power from the primary to the secondary.
The
voltage and current produced in the secondary will be a factor of the
relationship of the windings in the primary and the secondary.
Transformers may be used to step-up
8
OD1725




 Previous Page
Previous Page
