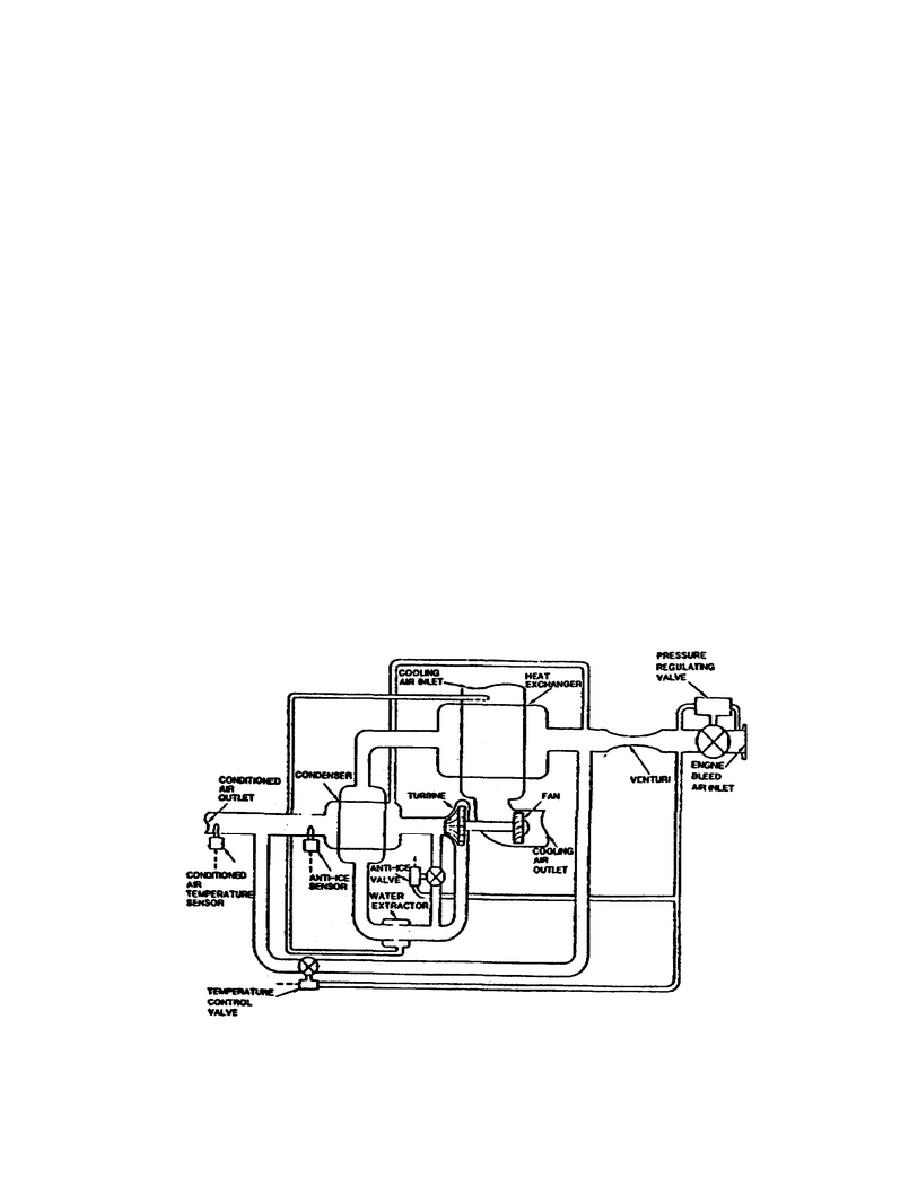
control point.
The controller electrically controls the
valve; air tapped off the duct (between the pressure
regulator and the flow limiting venturi) pneumatically
actuates the valve.
Distribution Temperature Control.
The previous paragraph
described
the
method
used
to
control
the
minimum
temperature of the air delivered; however, operating
conditions do not always require air delivered at that low
temperature.
To control the temperature, the system has
the conditioned air temperature sensor placed in the
distribution duct down stream of the condenser tapoff.
This sensor monitors the temperature of the air sent to the
distribution system.
If the tank commander selects a
delivery temperature of 70,F, the sensor sends a signal to
the controller indicating the temperature of the air
delivered and the controller compares this to the selected
temperature.
When the selected temperature is higher than delivered
temperature,
the
controller
sends
a
signal
to
the
temperature control valve that causes the valve to open,
the same as the anti-ice valve does when it receives a
signal.
The temperature control valve closes if the
temperature of the delivered air is higher than the
selected temperature.
The temperature control valve
controls the air flow from the tapoff before the heat
exchanger and allows it to mix with the turbine discharge
air sent to the final point.
Figure 1-3.
The Air Cycle System.
7
OD1705




 Previous Page
Previous Page
