BASIC ELECTRONICS - OD1633 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
(c) The total voltage across a series circuit is equal to the sum
of the individual voltage drops.
(d) The voltage drop across a resistor in a series circuit is
proportional to the ohmic value of the resistor.
(e) The total power in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the
individual powers used by each circuit component.
c. Series Circuit Analysis.
To establish a procedure for
solving
series circuits, the following sample problems will be solved.
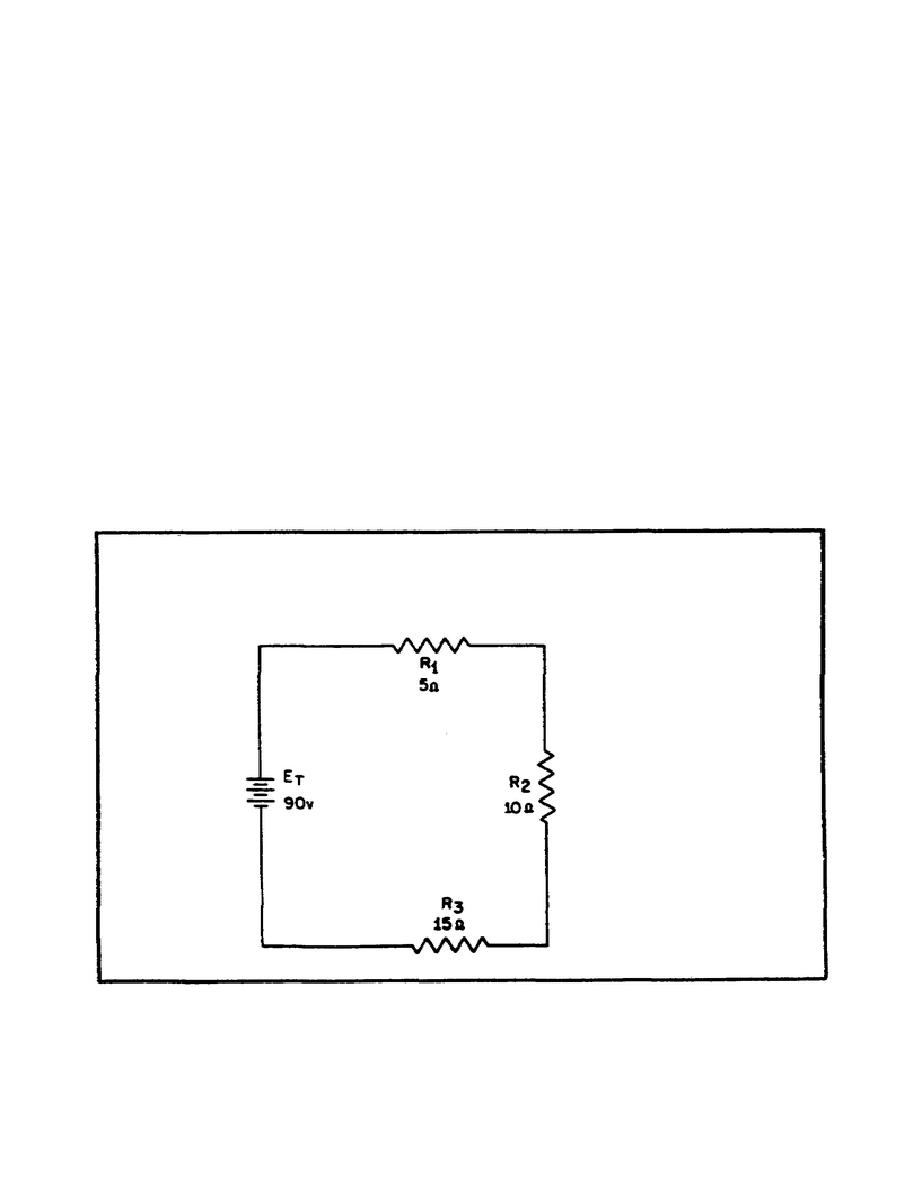
Example: Three resistors of 5 Ohms, 10 Ohms, and 15 Ohms are connected in
series with a power source of 90 volts as shows in figure 26.
Find the
total resistance, circuit current, voltage drop of each resistor, power of
each resistor, and the total power of the circuit.
In solving the circuit, the total resistance will be found first. Next, the
circuit current will be calculated. Once the current is known, the voltage
drops and power dissipations can be calculated.
FIGURE 26.
SOLVING FOR VARIOUS VALUES IN A SERIES CIRCUIT.
47




 Previous Page
Previous Page
