BASIC ELECTRONICS - OD1633 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
Given:
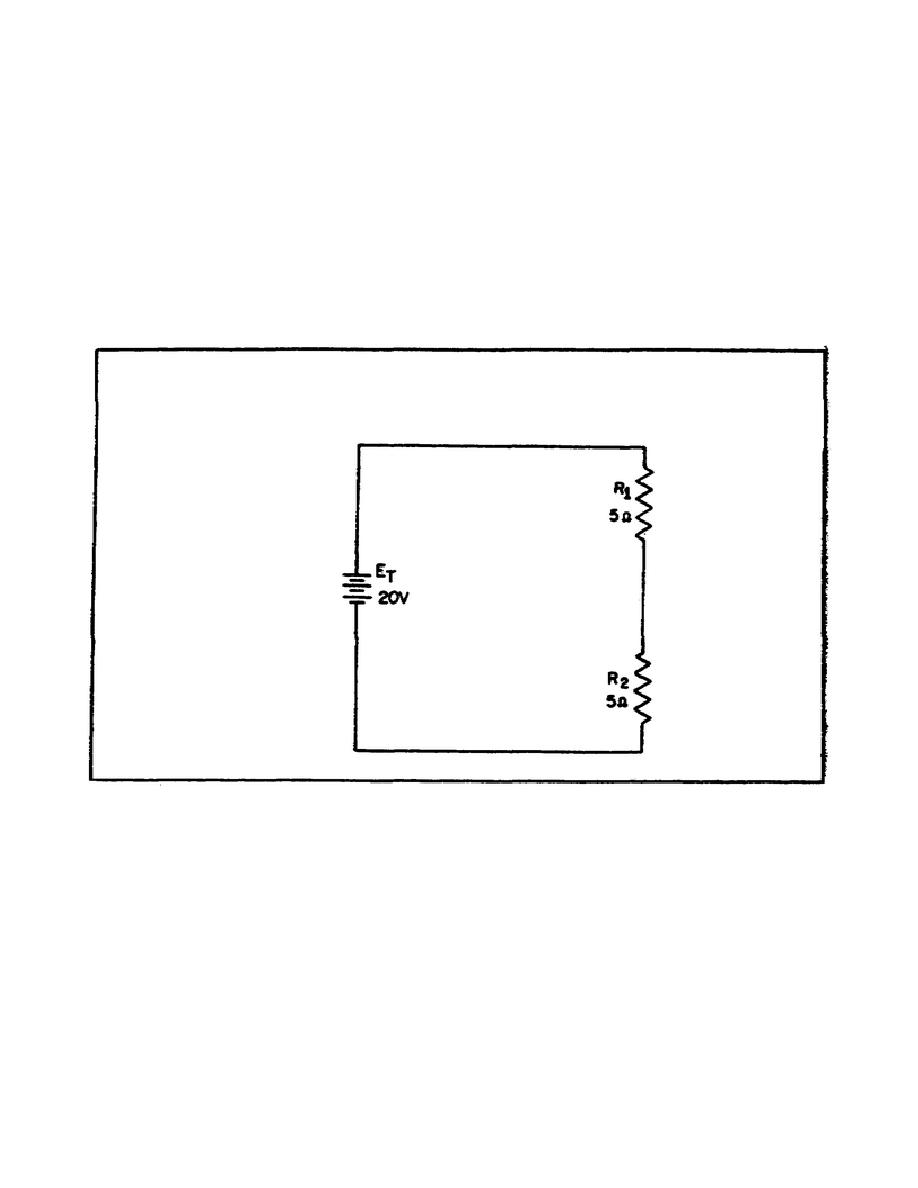
I1 = 2 amperes
R1 = 5 Ohms
Solution:
E1 = I1 x R1
E1 = 2 amperes x 5 Ohms
E1 = 10 volts
FIGURE 23.
CALCULATING INDIVIDUAL VOLTAGE DROPS IN A SERIES CIRCUIT.
By inspecting the circuit, you can see that R2 is the same ohmic value as R1
and carries the same current. The voltage drop across R2 is therefore also
equal to 10 volts. Adding these two 10 volt drops together gives a total
drop of 20 volts, exactly equal to the applied voltage.
For a series
circuit then:
ET = E1 + E2 + E3 + . . . En
Example: A series circuit consists of three resistors having values of 20
Ohms, 30 Ohms, and 50 Ohms, respectively. Find the applied voltage if the
current through the 30 Ohm resistor is 2 amperes.
42




 Previous Page
Previous Page
