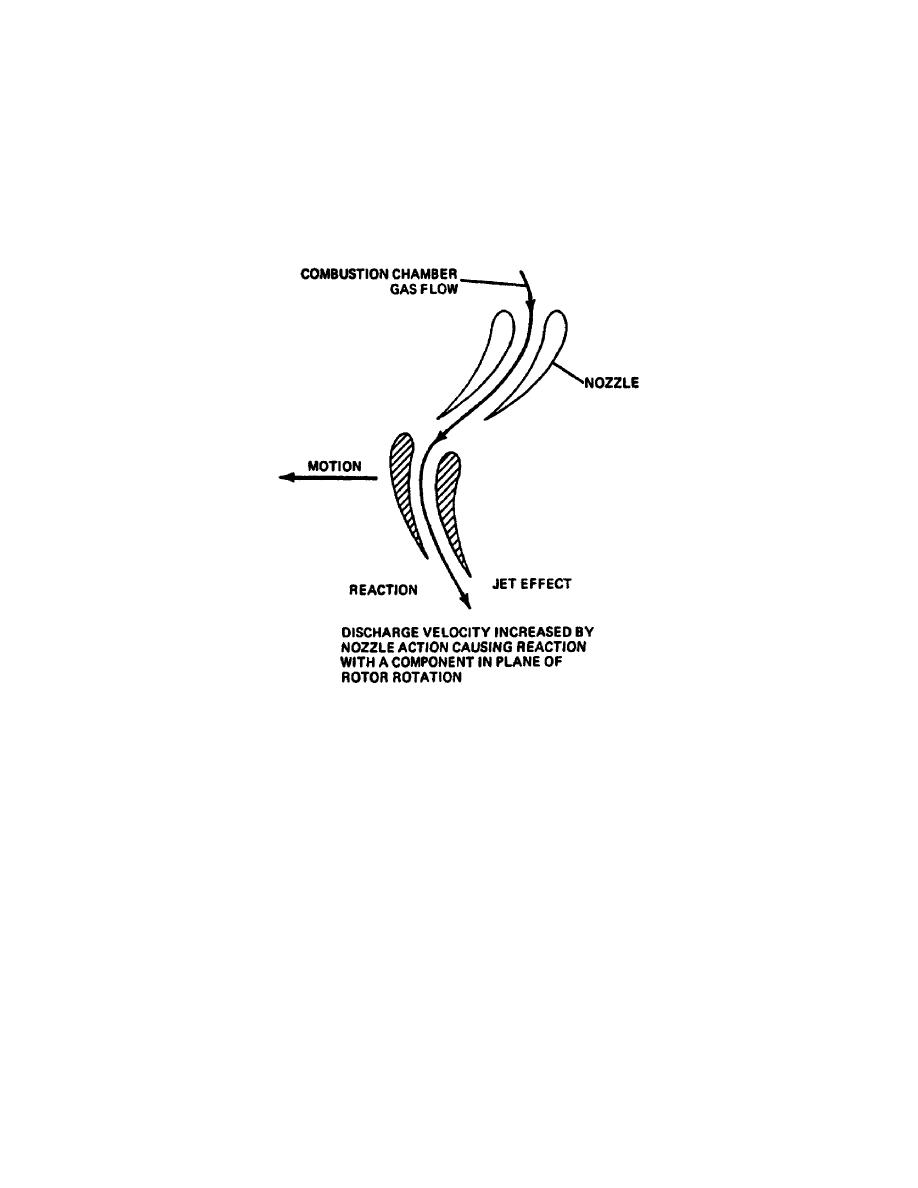
o Reaction. The reaction turbine operates on the differential
pressure principle much like the wing of an airplane (Figure 128). As the
gases enter a converging passageway on the firststage rotor, an increase in
velocity and a decrease in pressure is experienced. The result is a rotation
of the turbine wheel in the direction of low pressure. The reaction turbine
wheel, therefore, does not require relatively high entrance velocities as does
the impulse turbine.
Figure 128. Reaction Turbine.
o ImpulseReaction. The impulsereaction turbine blade is a
combination of both the impulse and reaction designs. The larger circumference
of the assembly at the ends of the turbine blades requires the tips to travel
at a faster rate of speed than the roots to obtain the same degree of rotation.
The impulsereaction type blade uses this concept to equalize the velocities of
the gases exiting the root and tip of the turbine wheel. This type is designed
so that the base of the blade is an impulse design and the tip is a reaction
design. This provides an equal pressure distribution across the blade and
therefore, an efficient turbine blade. The impulsereaction turbine blade is
used almost exclusively in modern turboshaft engines.
39
OD0610




 Previous Page
Previous Page
