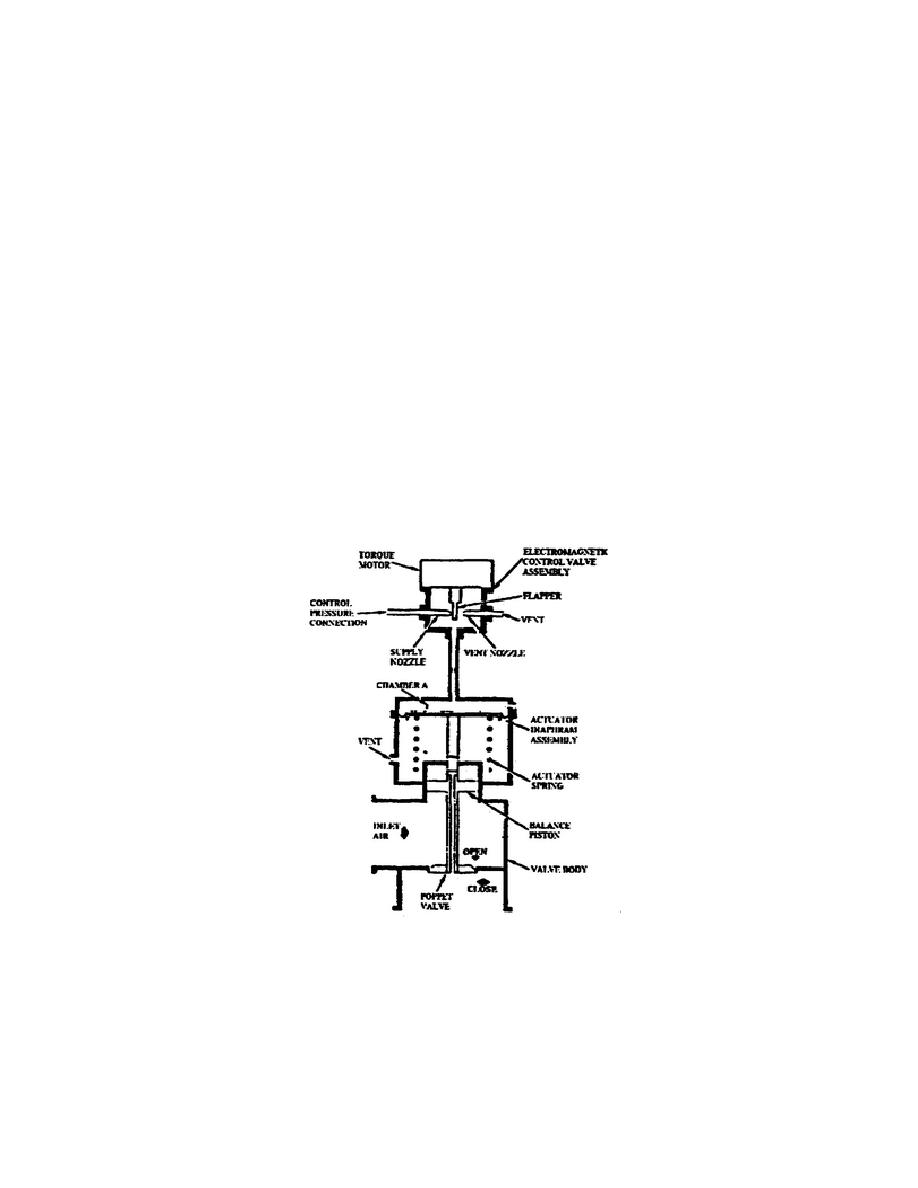
valve torque motor increases.
The torque motor moves the
flapper from the supply nozzle toward the vent nozzle. The
more the flapper moves, the more air it permits through the
supply nozzle and the less air it permits out the vent.
This causes the pressure in the torque motor to increase as
the current increases.
The opening chamber (chamber A)
also feels this increase in pressure and the valve moves
toward the open position as the pressure in the opening
chamber builds and overcomes the spring pressure holding
the valve closed.
As the signal from the controller changes causing the valve
to close, the current flow in the torque motor decreases
and the flapper moves toward the supply nozzle and away
from the vent nozzle.
This causes the pressure in the
opening chamber to decrease and the valve moves toward the
closed position.
Failure Mode. If the torque motor does receive current, or
the valve fails to move from the supply port, or the valve
does receive pressure at the supply port, or if the
diaphragm in the actuator ruptures, the valve stays closed
causing the condenser to ice.
Figure 1-37.
Temperature Control Valve Schematic.
14.
Conditioned Air Temperature Sensor (fig. 1-38).
The NBC system has the conditioned air temperature sensor located in
the recirculation and mixing duct just downstream of the junction
from the temperature control valve. Except for the
32
OD1705




 Previous Page
Previous Page
