BASIC ELECTRONICS - OD1633 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
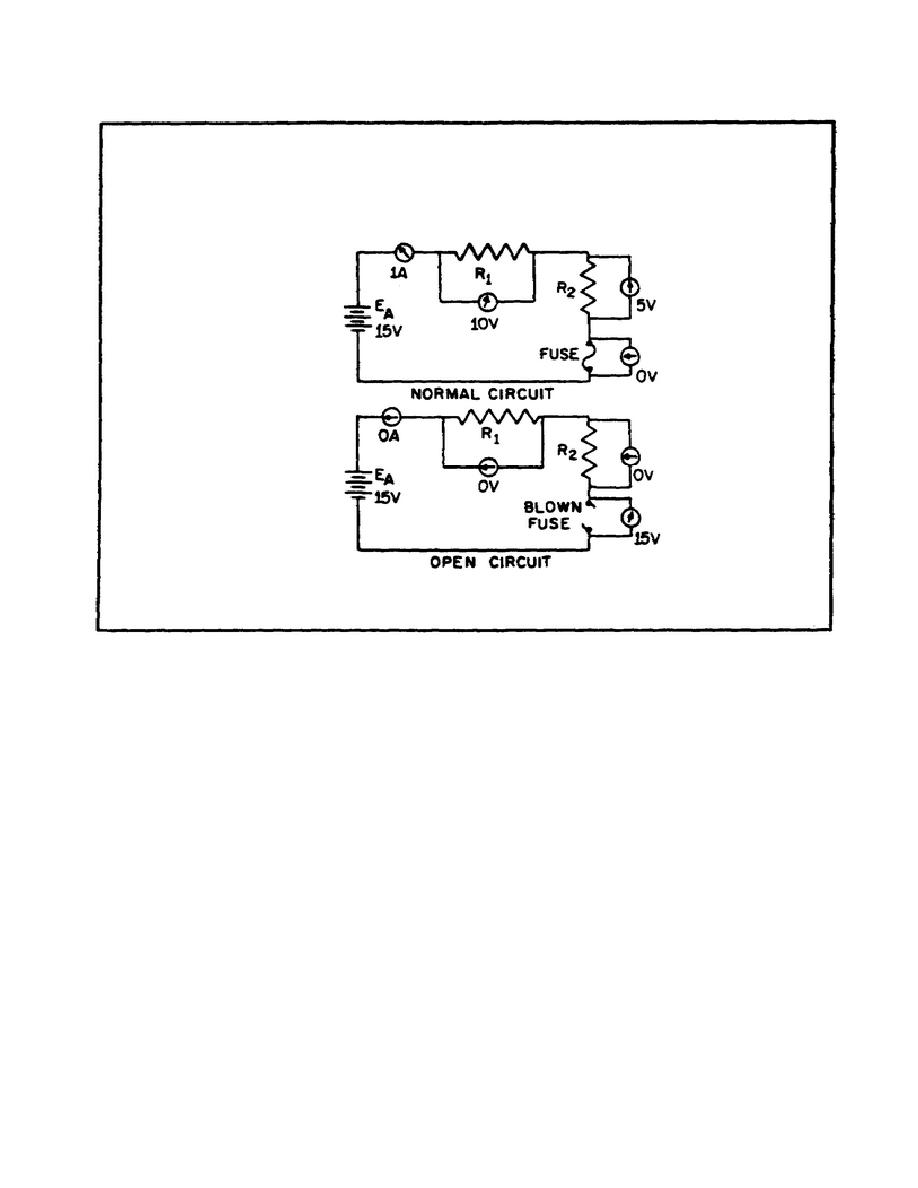
FIGURE 37.
NORMAL AND OPEN CIRCUIT CONDITIONS.
NORMAL CURRENT (A)
EXCESSIVE CURRENT (B).
c. Short Circuit.
A short circuit is an accidental path of low
resistance which passes an abnormally high amount of current.
A short
circuit exists whenever the resistance of a circuit or the resistance of a
part of a circuit drops in value to almost zero Ohms. A short often occurs
as a result of improper wiring or broken insulation.
In figure 38 (on the following page), a short is caused by improper wiring.
Note the effect on current flow.
Since the resistor has in effect been
replaced with a piece of wire, practically all the current flows through the
short and very little current flows through the resistor R1. Electrons flow
through the short (a path of almost zero resistance) and the remainder of
the circuit passes through the 10 Ohm resistor and the battery. The amount
of current flow increases greatly because its resistive path has decreased
from 10,010 Ohms to 10 Ohms.
Due to excessive current flow, the 10 Ohm
resistor becomes heated.
As it attempts to dissipate this heat, the
resistor will probably be destroyed.
Figure 39 (on the following page)
shows a pictorial wiring diagram, which indicates how broken insulation
might cause a short circuit.
62




 Previous Page
Previous Page
