ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES - OD1647 - LESSON 1/TASK 1
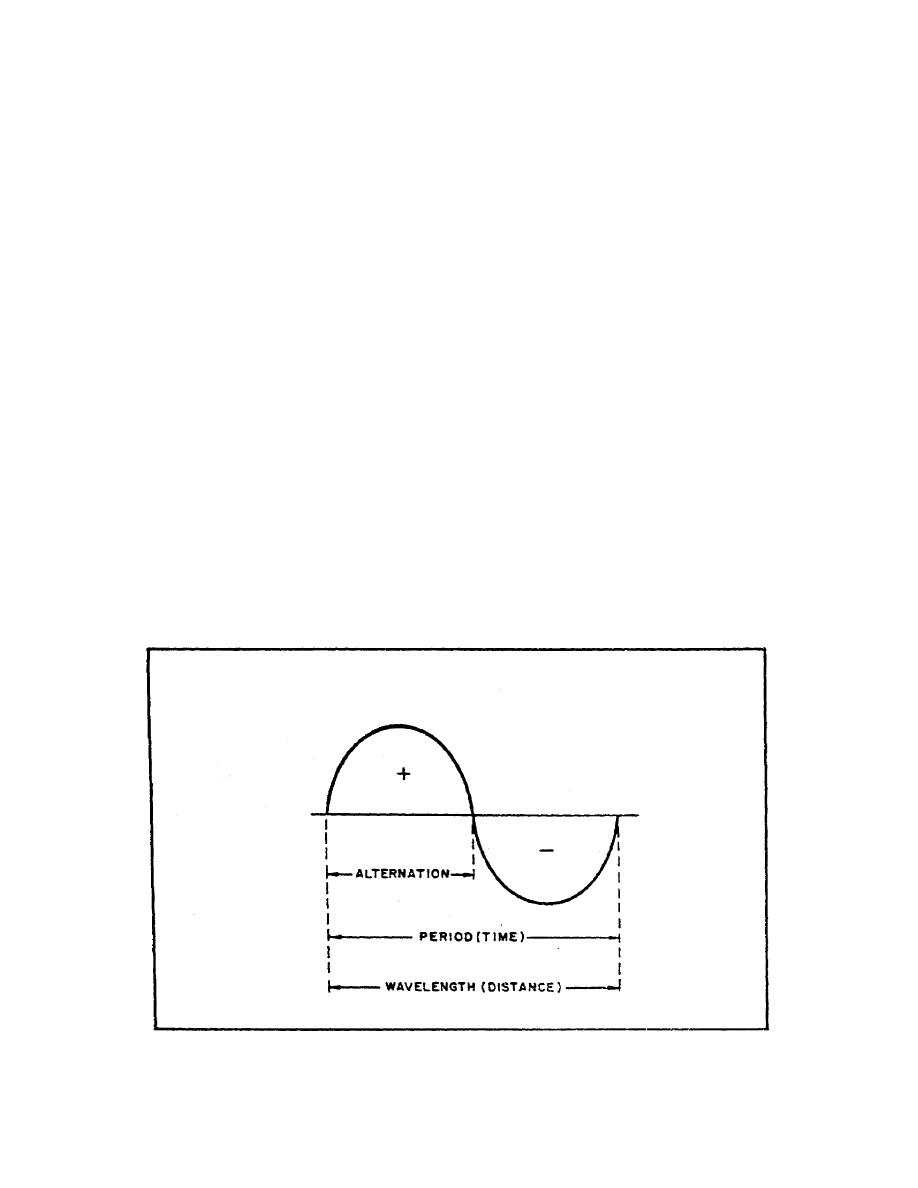
Each cycle of the sine wave shown in figure 61, on the previous
page, consists of two identically shaped variations in voltage.
The variation which occurs during the time the voltage is
positive is called the POSITIVE ALTERNATION. The variation
which occurs during the time the voltage is negative is called
the NEGATIVE ALTERNATION. In a sine wave, these two
alternations are identical in size and shape, but opposite
polarity.
The distance from zero to the maximum value of each alternation
is called the AMPLITUDE. The amplitude of the positive
alternation and the amplitude of the negative alternation are
the same.
h. Wavelength. The time it takes for a sine wave to complete
one cycle is defined as the period of the waveform. The
distance traveled by the sine wave during this period is
referred to as WAVELENGTH. The wavelength is the distance along
the waveform from one point to the same point on the next cycle.
You can observe this relationship by examining figure 62. The
point on the waveform where measurement of the wavelength begins
is not important as long as the distance is measured to the same
point on the next cycle (figure 63 on the following page).
FIGURE 62. WAVELENGTH.
91




 Previous Page
Previous Page
