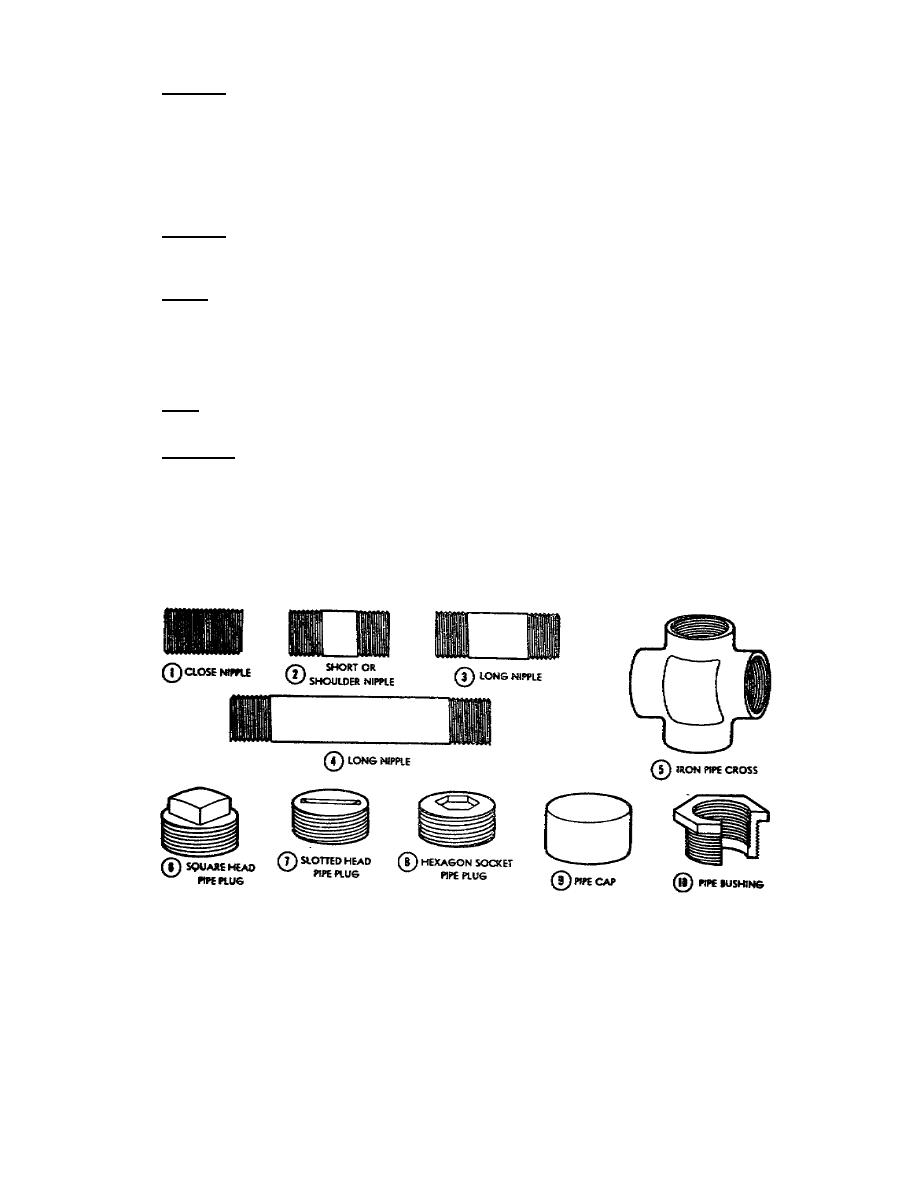
g. Nipples. A nipple is a piece of pipe, 12 inches or less in length,
threaded on both ends, and used to make an extension from a fitting or to join two
fittings. A close nipple (1, fig 6), threaded its entire length, joins two
fittings which must be very close to each other. A nipple threaded nearly its
entire length with only a short unthreaded section in the center is called a short
or shoulder nipple (2, fig 6). When the unthreaded portion is longer, the nipple
is called a long nipple and sometimes an extra long nipple (3 and 4, fig 6). Long
and extra long nipples are specified by length such as 4 inches, 6 inches, etc.
h. Crosses. An iron pipe cross (5, fig 6) is an ordinary T with an additional
back outlet opposite the branch outlet. The axes of the four outlets are in the
same plane and perpendicular to each other. Crosses are made in many sizes.
i. Plugs. Iron pipe plugs have male threads used to close openings in other
fittings and have various types of heads. The square head (6, fig 6) is the most
widely used; the slotted head (7, fig 6) is seldom used except in close spaces
where a wrench cannot be used; and the hexagon socket head (8, fig 6) is used where
a bulge would cause difficulty, as in a boiler or hot water storage tank fitted
with an insulating jacket.
j. Caps. A pipe cap (9, fig 6) is a fitting with a female thread used like a
plug except that the cap fits on the male end of a pipe or nipple.
k. Bushings. A bushing has male thread on the outside and female thread on
the inside. It is generally used to connect the male end of a pipe to a larger
fitting. The ordinary bushing (10, fig 6) has a hexagon nut at the female end for
screwing the bushing into the fitting. The faced bushing, without a hexagon nut,
is used for very close work.
Figure 6.
Miscellaneous iron pipe fittings.
57




 Previous Page
Previous Page
