ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES - OD1647 - LESSON 1/TASK 1
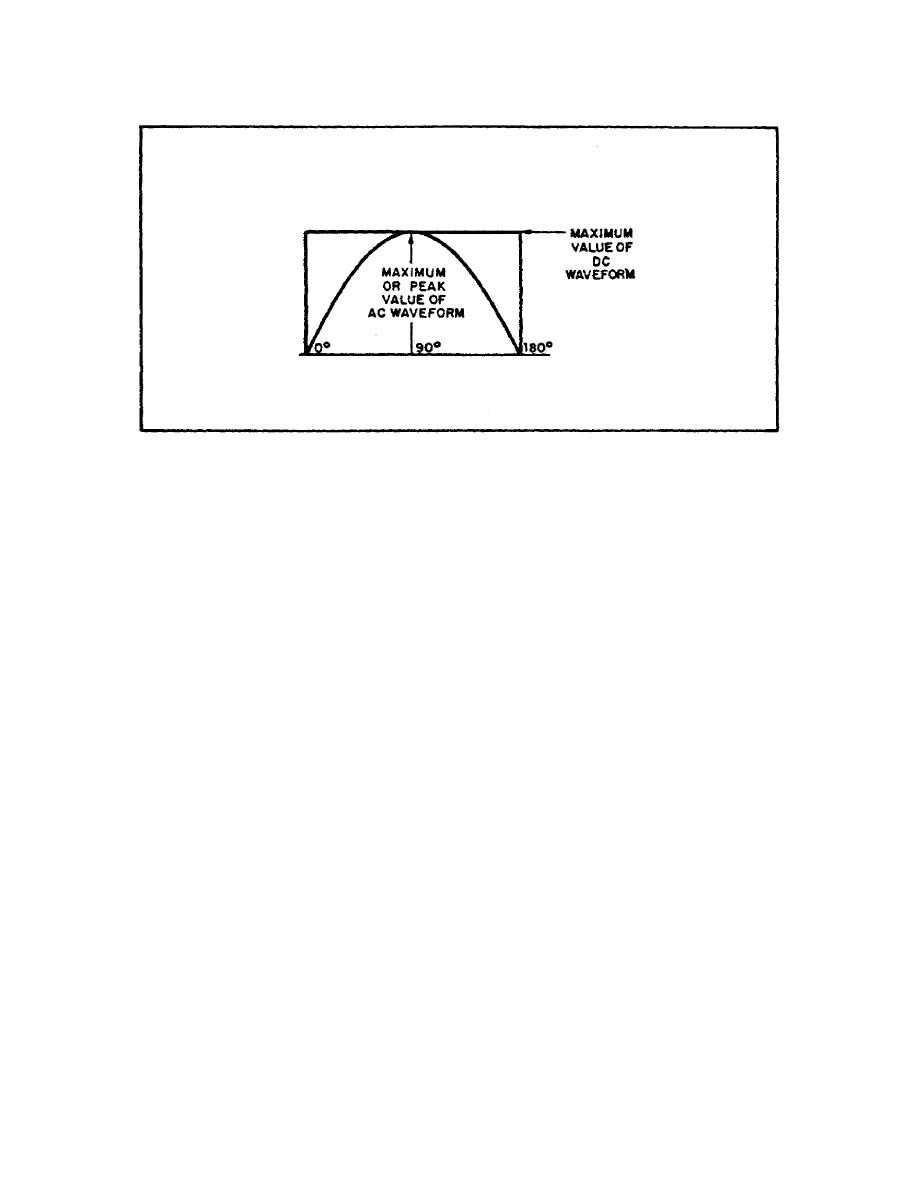
FIGURE 64. MAXIMUM OR PEAK VALUE.
During each complete cycle of ac there are always two maximum or
peak values, one for the positive halfcycle and the other for
the negative halfcycle. The difference between the peak
positive value and the peak negative value is called the peak
topeak value of the sine wave. This value is twice the maximum
or peak value of the sine wave and is sometimes used for
measurement of ac voltages. Note the difference between peak
and peaktopeak values in figure 65 on the following page.
Usually alternating voltage and current are expressed in
EFFECTIVE VALUES rather than in peaktopeak values.
(2) Instantaneous Value. The INSTANTANEOUS value of an
alternating voltage or current is the value of voltage or
current at one particular instant. The value may be zero if the
particular instant is the time cycle at. which the polarity of
the voltage is changing. It may also be the same as the peak
value, if the selected instant, is the time in the cycle at
which the voltage or current stops increasing and starts
decreasing. There are actually an infinite number of
instantaneous values between zero and the peak value.
(3) Average Value. The AVERAGE value of an alternating
current or voltage is the average of ALL the INSTANTANEOUS
values during ONE alternation. Since the voltage increases from
zero to peak value and decreases back to zero during one
alternation, the average value must be some value
93





 Previous Page
Previous Page
