BASIC ELECTRONICS - OD1633 - LESSON 1/TASK 1
The ability of the resistor to dissipate heat depends upon the design of the
resistor itself being dependent on the amount of surface area which is
exposed to the air. A resistor designed to dissipate a large amount of heat
must therefore have a large physical size. The heat dissipating capability
of a resistor is measured in watts.
A watt is the practical unit of
electrical power. It is the amount of power used when one ampere of direct
current (dc) flows through a resistance of one Ohm. Some of the more common
wattage ratings of carbon resistors are: one-eighth watt, one-fourth watt,
one-half watt, one watt, and two watts. In some of the newer state-of-the-
art circuits of today, much smaller wattage resistors are used. The higher
the wattage rating of the resistor, the larger is the physical size.
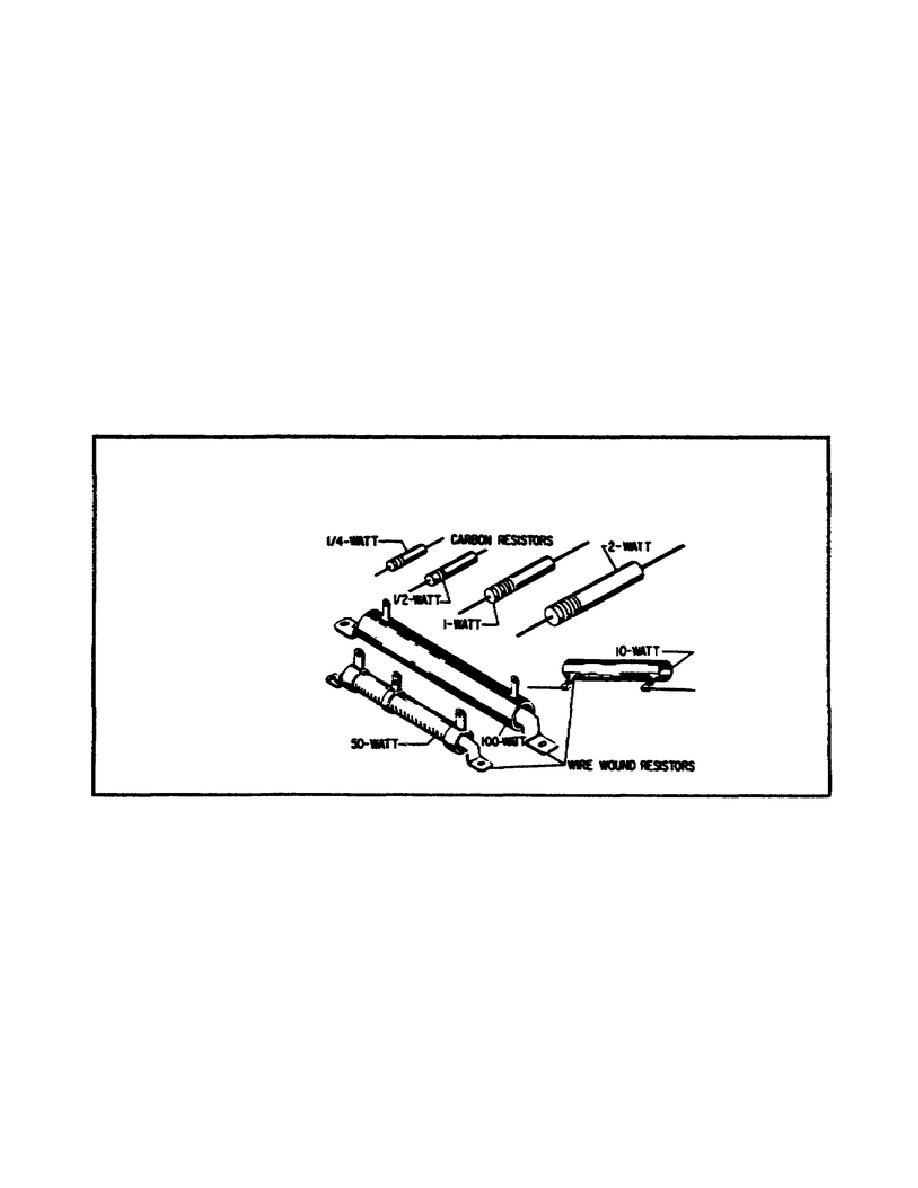
Resistors that dissipate very large amounts of power (watts) are usually
wirewound resistors.
Wirewound resistors with wattage ratings up to 50
watts are not uncommon. Figure 9 shows some resistors which have different
wattage ratings. Notice the relative sizes of the resistors.
FIGURE 9.
RESISTORS OF DIFFERENT WATTAGE RATINGS.
d. Standard Color Code System. In the standard color code system, four
bands are painted on the resistor, as shown in figure 10 on the next page.
The color of the first band indicates the value of the first significant
digit. The color of the second band indicates the value of the second
20




 Previous Page
Previous Page
