USE/CARE OF HANDTOOLS & MEASURING TOOLS - OD1621 - LESSON 2/TASK 2
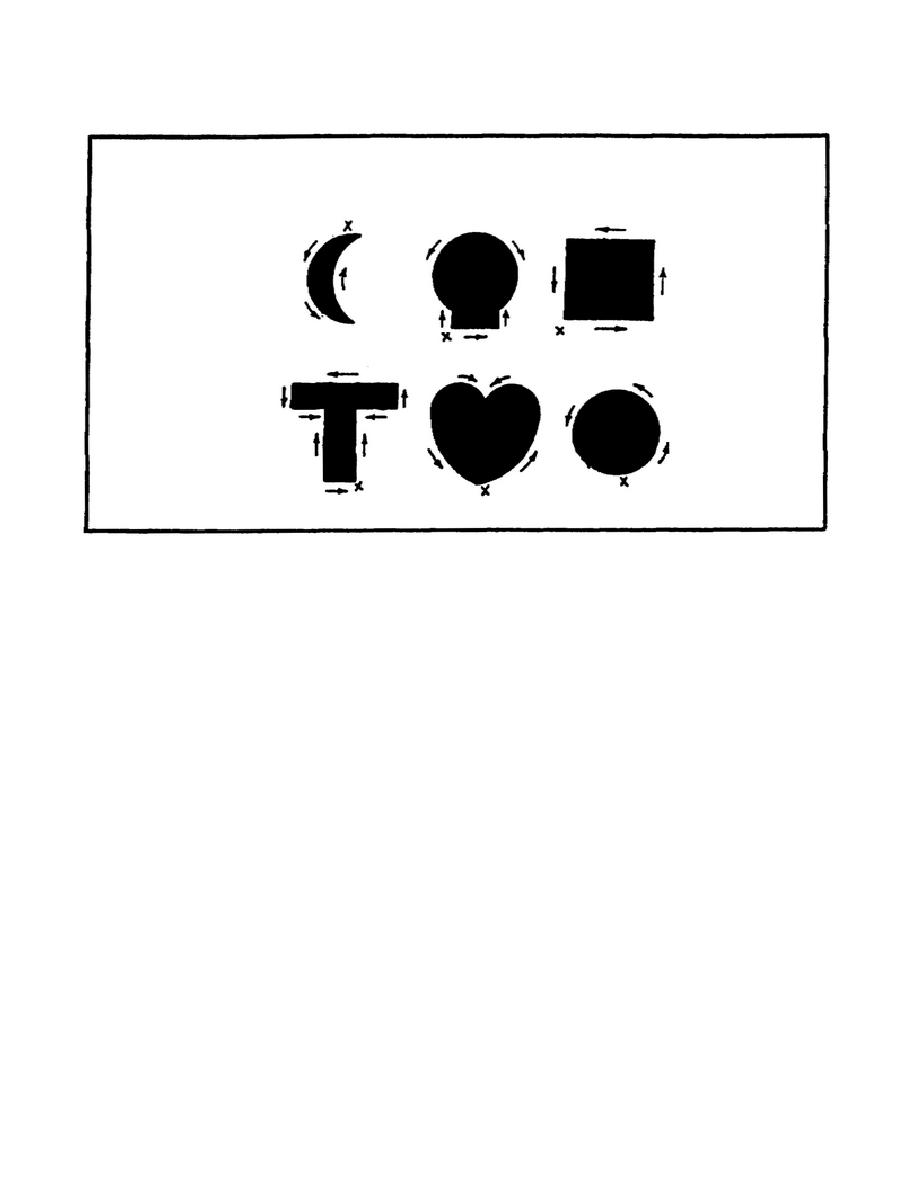
FIGURE 115.
DIRECTION OF CUTTING SHAPES WITH SHEARS.
hollow punch or small cold chisel and punch a hole large enough for the
point of the curved blade or hawk bill shears to be inserted. Complete the
cut with the points of the curved shears.
d. Care of Shears.
(1) Care and Cleaning. Keep tools clean at all times. Lubricate the
pivot screw or bolt with a drop of light oil.
Remove rust with a fine
aluminum oxide abrasive cloth. Apply a thin film of oil on tools to prevent
rust. Hang tools on hooks or place them on a shelf when not in use. Never
throw tools in a box where the cutting edges may be damaged. Do not attempt
to cut material heavier than the tools are designed to handle.
Never use
shears as a hammer, or as a pry bar, since they are easily damaged.
For
long periods of storage, coat tools with a rust preventive compound and
store them in a dry place where the cutting edges do not come in contact
with other metal objects.
(2) Sharpening. Dull shears can usually be sharpened on an oilstone
or with a file, without grinding.
Never grind shears if sharpening will
suffice, since most shears become useless after two or three grindings. To
sharpen with a file, clamp shears in a vise and use a flat file, as shown in
figure 116 on the following page. The flat file is used on beveled edges
only--not on the flat faces
150




 Previous Page
Previous Page
