USE/CARE OF HANDTOOLS & MEASURING TOOLS - OD1621 - LESSON 2/TASK 2
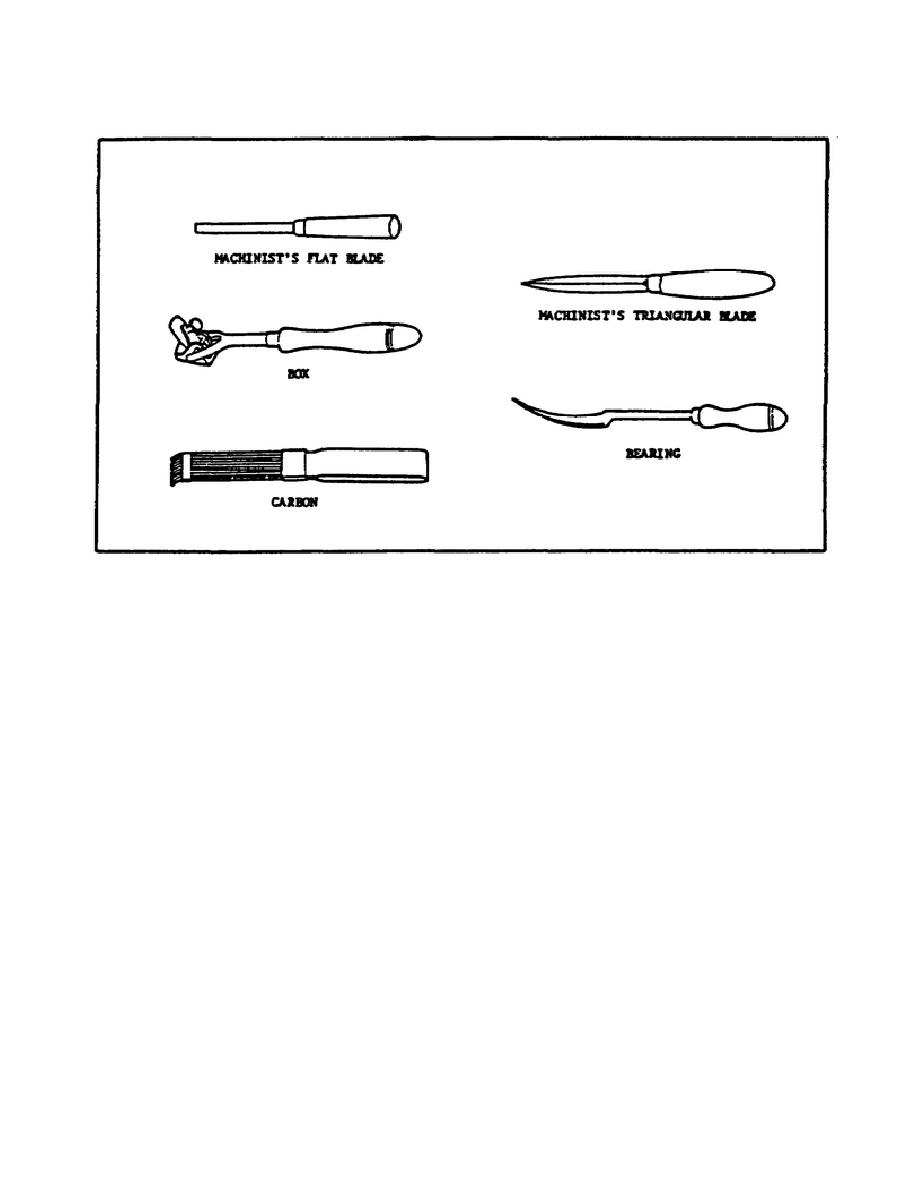
FIGURE 108.
TYPES OF SCRAPERS.
c. Use of Scrapers.
(1) Preparing Work Before Scraping.
(a) Do not attempt to scrape off three or four thousandths of an
inch of metal on a large surface.
(b) Surfaces that are to be made flat should be checked against a
surface plate.
A curved surface should be checked against its mating
surface.
Be sure that both the surface to be scraped and the reference
surface are perfectly clean. Apply a very thin film of prussian blue on the
reference surface. To determine the high spots on the work, lightly rub the
work against the blued reference surface. Remove the work and examine for
any blue spots.
The prussian blue transferred to the work will indicate
where scraping is required. Scrape and rematch the work to the reference
surface until the work surface is covered with uniform coating of blue.
(c) Visible burrs should be removed by filing before beginning the
scraping process.
(2) Using a Carbon Scraper.
The carbon scraper is used to clean
carbon deposits from cylinder heads, pistons, and other metal surfaces where
carbon accumulates.
The blades are fairly dull to prevent scoring of a
piston and cylinder wall.
139




 Previous Page
Previous Page
