USE/CARE OF HANDTOOLS & MEASURING TOOLS - OD1621 - LESSON 2/TASK 1
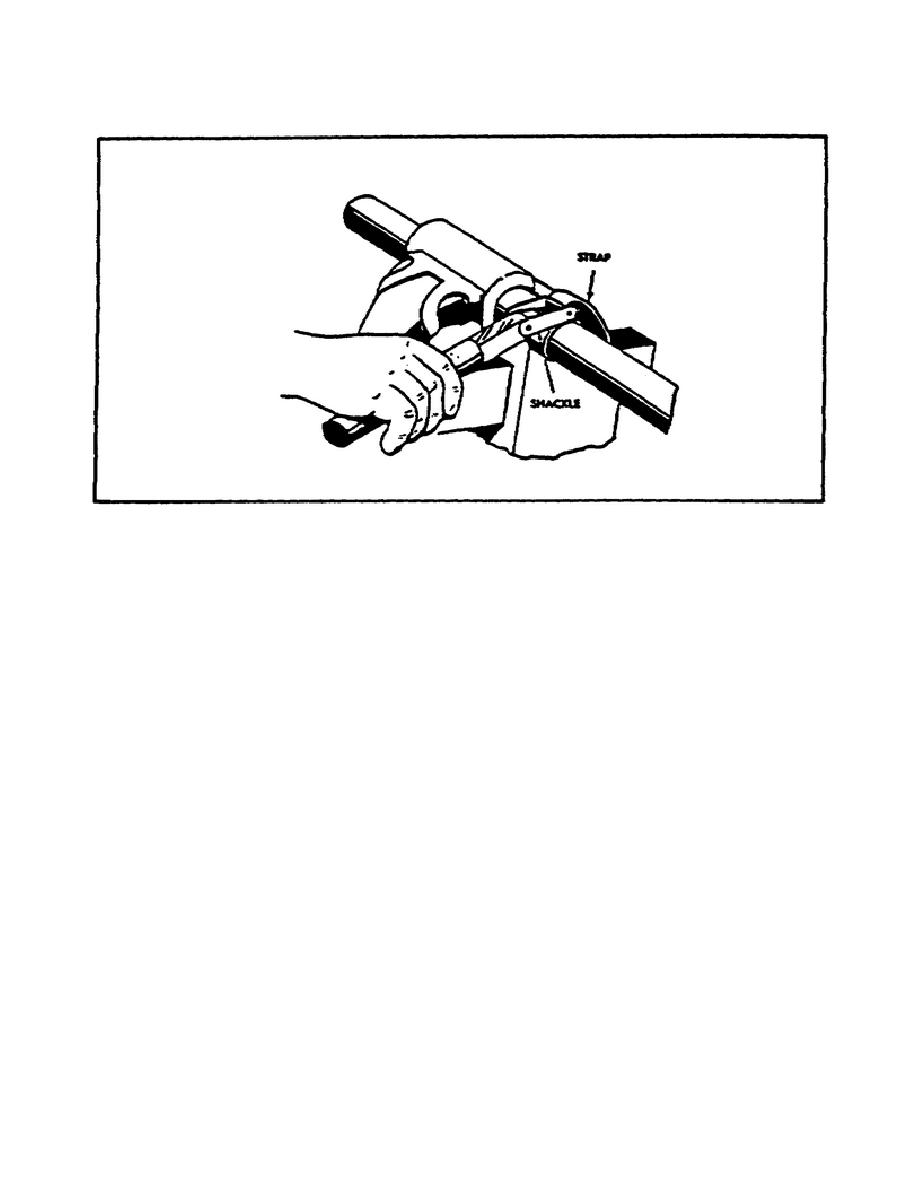
FIGURE 28.
USING A STRAP PIPE WRENCH.
jaw when looped around the pipe, gripping the pipe on the entire outer
circumference. It is used for rough pipework on very large diameter pipes.
(8) Torque Wrench. A torque wrench enables you to set up a nut or
bolt when the force applied to the handle reaches the specified limit.
Manufacturers' instructions specify these limits of turning force. Cylinder
head nuts and bolts, rod bearing cups, and other places on automotive and
airplane engines usually require torque wrench limits. Select a proper size
socket wrench and attach it to the torque wrench square drive. Place the
socket wrench on the work and pull the torque wrench handle in the desired
direction to tighten the work. The tightening torque will be indicated on
the dial or scale, depending on the type of torque wrench used.
(9) Spanner Wrenches. When using a pin-face spanner wrench (figure
29 on the following page), insert the pins or lugs into the pin holes of the
part. Keep the pin face of the wrench flush with the part surface and turn
the wrench. Exert enough force against the wrench so that the pins do not
jump out of the holes. Hose coupling spanner wrenches are shaped so that
they fit around the coupling with the pin or lug at right angles to the
handle.
Insert the pin in the hose coupling pin hole.
Pull or push the
handle in the direction opposite the hook of the spanner wrench.
Make
certain the pin fits the hole and that the force is
45




 Previous Page
Previous Page
