PRINCIPLES GASOLINE/DIESEL FUEL SYSTEMS - OD1620 - LESSON 1/TASK 2
piston pushes the piston down, which in turn pushes the power valve open.
The power jet is sometimes referred to as the economizer and the vacuum
piston as the step-up or power piston.
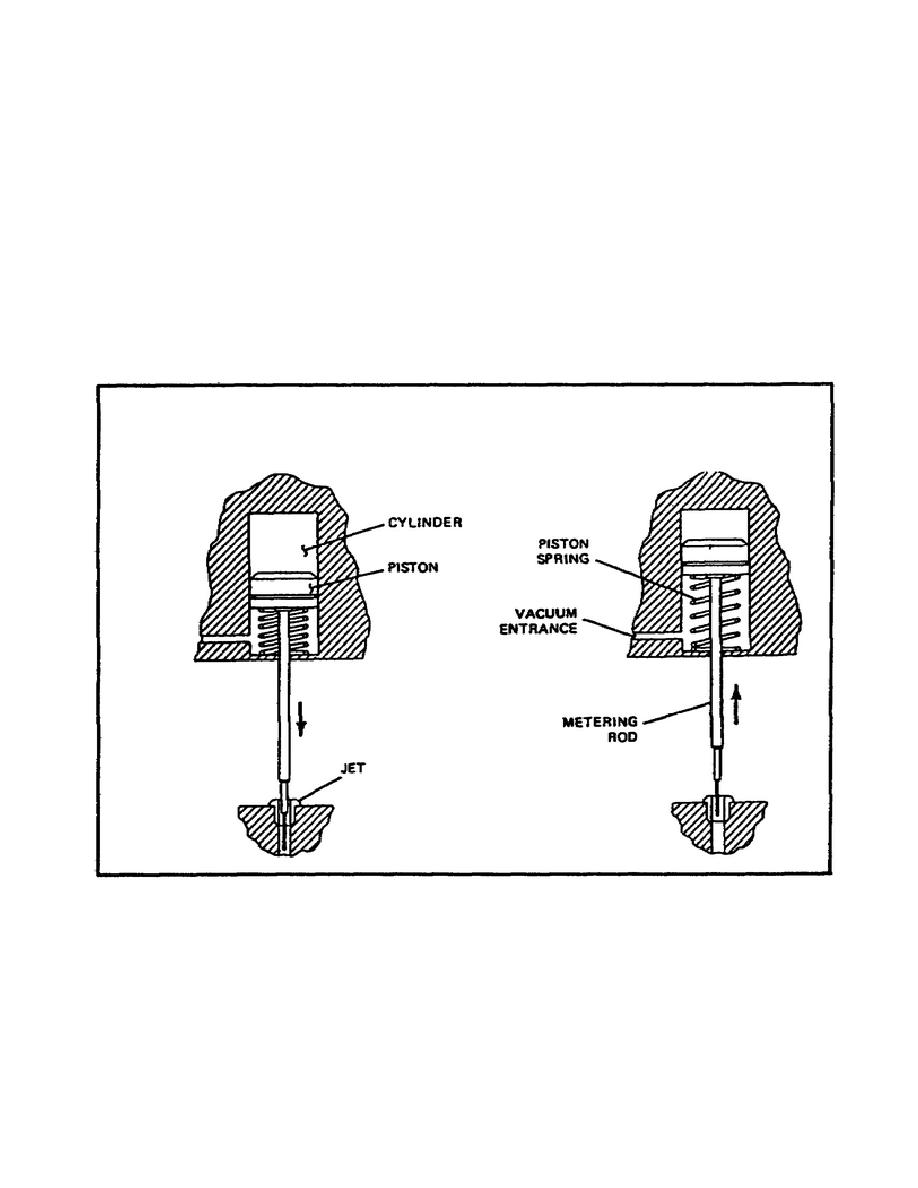
(b) Vacuum-Operated Metering Rod (figure 18). The vacuum-operated
metering rod uses a rod with a diameter that gets progressively larger in
steps from its end. The vacuum piston operates the metering rod. When the
engine load is light and manifold vacuum is high, the piston pushes the
metering rod into the jet against spring pressure, restricting the flow to
the discharge tube.
When the load demand increases, the manifold vacuum
decreases, causing the piston spring to lift the metering rod out of the
jet, progressively increasing the fuel flow to the discharge tube.
FIGURE 18.
VACUUM-OPERATED OPERATED METERING ROD.
(c) Mechanically-Operated Metering Rod (figure 19 on the following
page). The mechanically operated metering rod works by the same principles
as the vacuum-operated metering rod, except that it is operated by linkage
from the throttle valve. The linkage is calibrated so that the metering rod
regulates the fuel perfectly for each throttle position.
30




 Previous Page
Previous Page
