PRIN. OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES - OD1619 LESSON 2/TASK 3
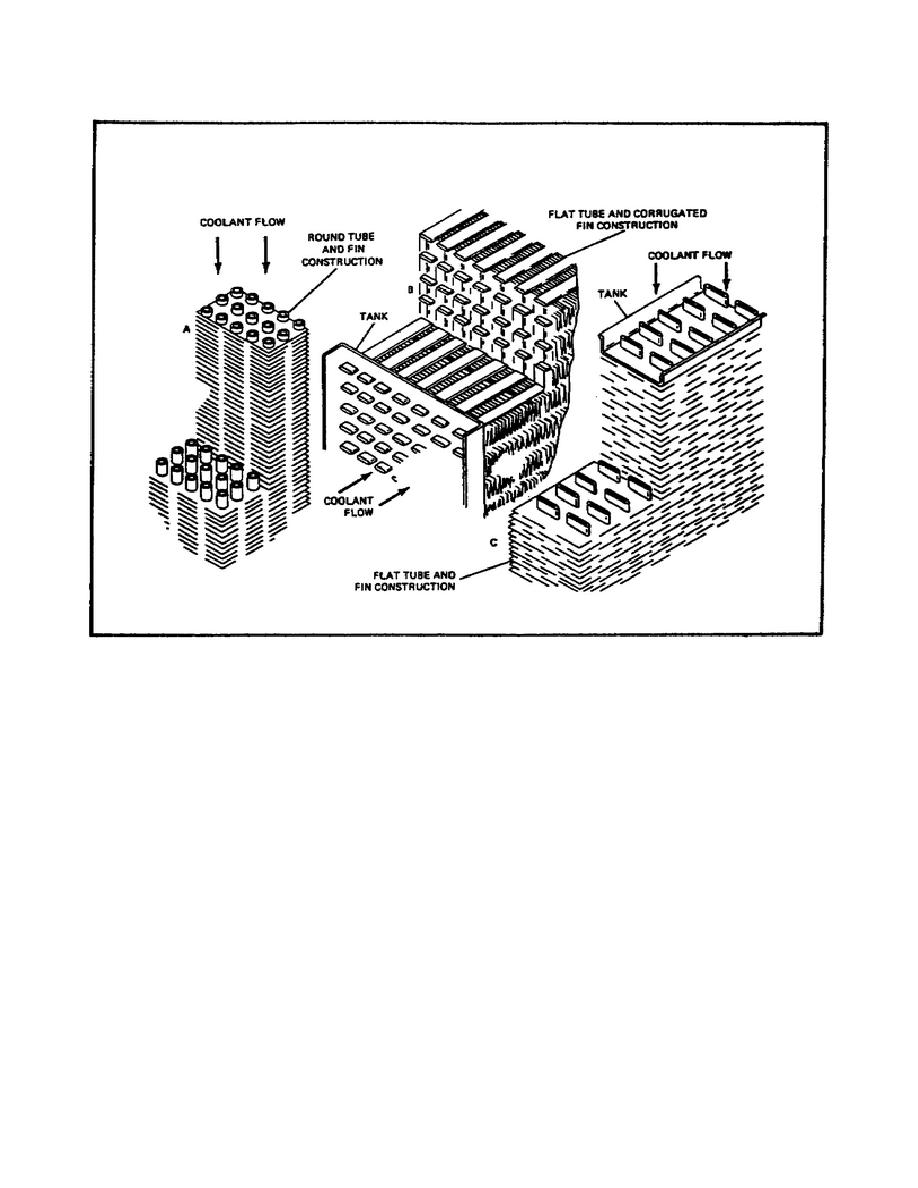
FIGURE 65.
ENGINE RADIATOR CONSTRUCTION.
into the atmosphere.
The dissipation of the heat from the fins is aided by
directing a constant airflow between the tubes and over the fins.
(3) The lower tank collects the coolant from the core and discharges it to the
engine through the outlet pipe.
(4) The overflow pipe provides an opening from the radiator for escape of coolant
or steam if pressure in the system exceeds the regulated maximum.
This prevents
rupture of cooling system components.
Some radiators are designed with their tanks on the sides in a vertical position.
They are connected by a core that contains horizontal tubes.
This radiator
configuration is called a crossflow radiator and operates in the same manner as the
conventional vertical flow radiator, though it should be noted that there is no
thermosiphon effect with a crossflow radiator.
e. Water Pump (figure 66 on the following page).
All modern cooling systems have
water pumps to
84




 Previous Page
Previous Page
