Lesson 1
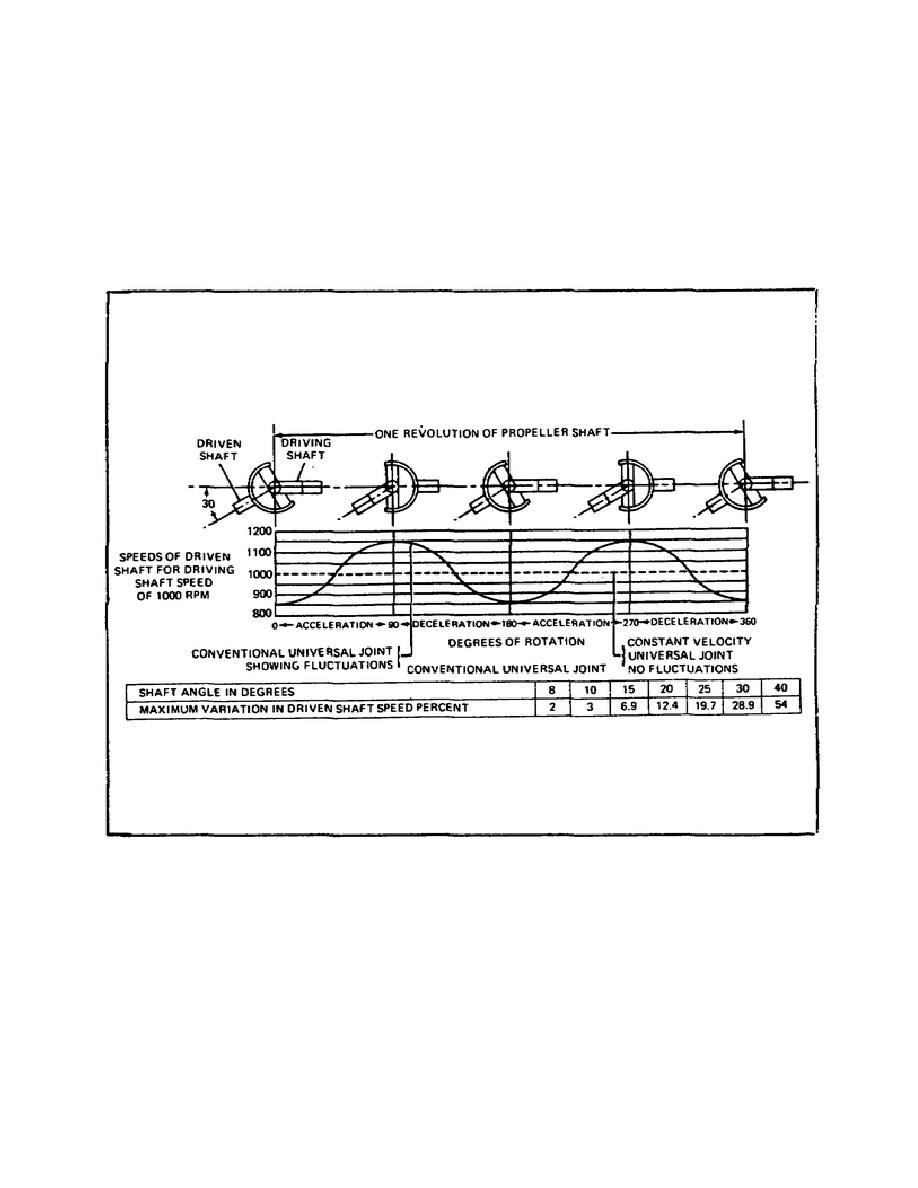
Universal joints must be designed so as to overcome a natural disadvantage of rotation at
an angle. A simple conventional universal joint causes the driven shaft to speed up and
slow down twice during each turn with respect to the driving shaft. The amount of
change (fluctuation) in speed depends on the amount of the angle between the two shafts.
As the angle between the driving and driven shaft is increased, the speed changes
increase.
FIGURE 4. SPEED FLUCTUATION CHART.
When the shafts are at a 30 angle, the fluctuation in speed is at maximum, about 30
percent of the driving speed. Notice that the driving shaft speed fluctuates between 850
and 1,150 RPM. If these speed fluctuations were transmitted to the axle assemblies,
stress would be placed on power train parts. In addition, a steady force would not be
applied to the driving wheels.
Speed fluctuations cannot be eliminated with a simple universal joint, but the effect is
reduced by using two joints (one at each end of the shaft). Fluctuations created by one
joint will be canceled out by the other.
5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
