ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES - OD1647 - LESSON 1/TASK 1
following discussion so that, a stepbystep analysis can be
made.
At the instant the switch is thrown to position 2 (figure 31,
view B, on the previous page), a displacement of electrons
occurs simultaneously in all parts of the circuit. This
electron displacement is directed away from the negative
terminal and toward the positive terminal of the source (the
battery). A brief surge of current will flow as the capacitor
charges.
If it were possible to analyze the motion of the individual
electrons in this surge of charging current, the following
action would be observed (figure 32).
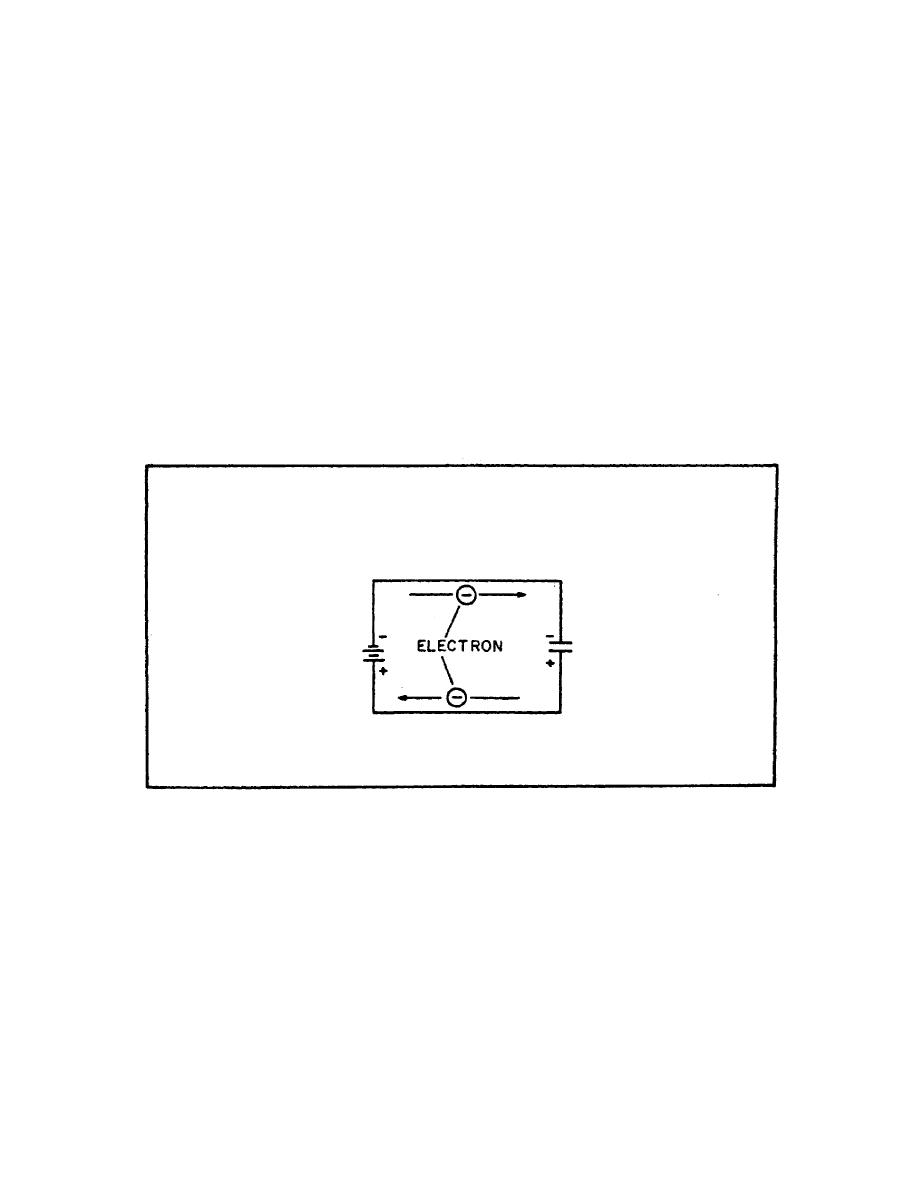
FIGURE 32. ELECTRON MOTION DURING CHARGE.
At the instant the switch is closed, the positive terminal of
the battery extracts an electron from the bottom conductor. The
negative terminal of the battery forces an electron into the top
conductor. At this instant, an electron is forced into the top
plate of the capacitor and another is pulled from the bottom
plate. Thus, in every part of the circuit a clockwise
DISPLACEMENT of electrons occurs simultaneously.
49




 Previous Page
Previous Page
