PRIN. OF INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINES - OD1619 LESSON 1/TASK 2
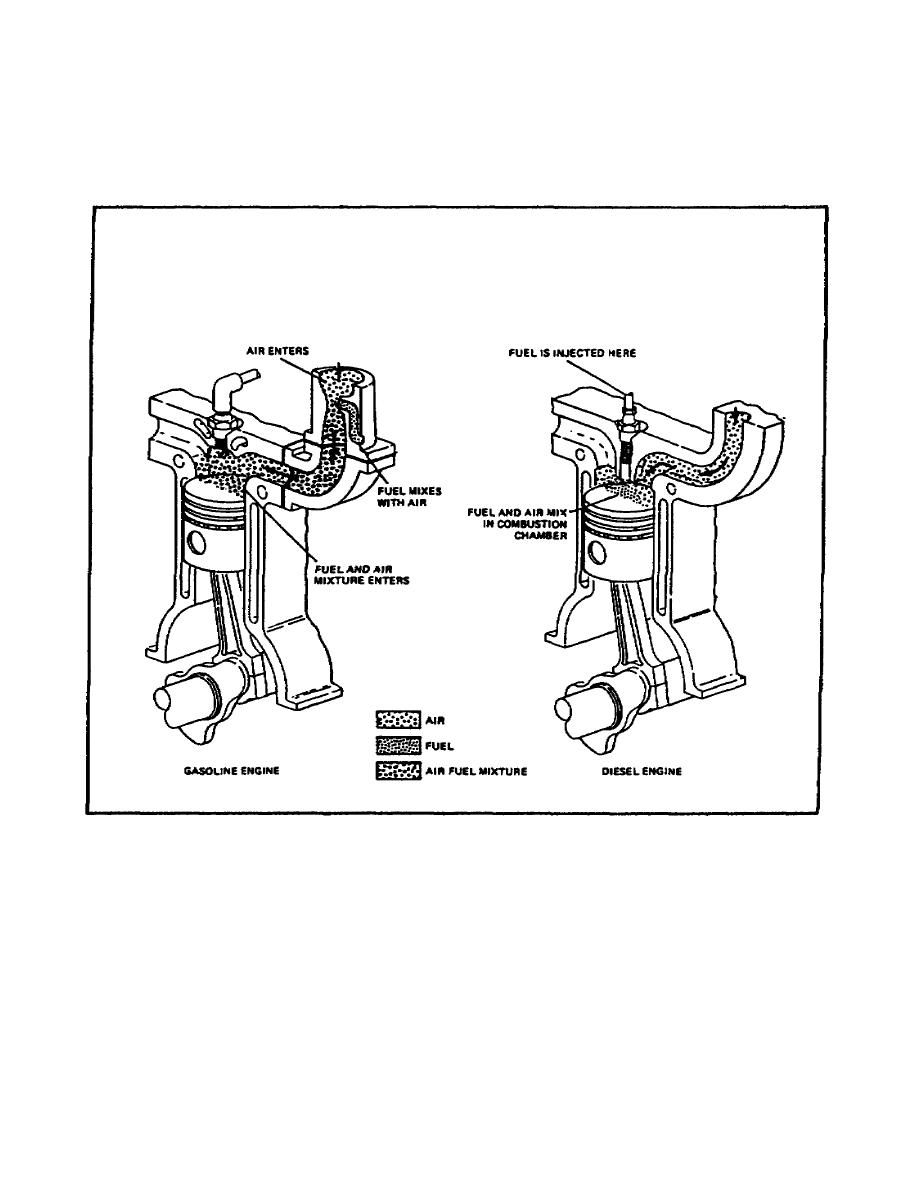
amount of air is constant. This contrasts with the gasoline engine where the speed
and power output are regulated by limiting the air entering the engine. This
comparison is illustrated in figure 28 on the following page.
FIGURE 27. COMPARISON OF DIESEL AND
GASOLINE ENGINE INTAKE
STROKES.
b.
Operation.
(1) Intake (figure 29, view A, on page 32). The piston is at top dead center at
the beginning of the intake stroke. As the piston moves downward, the intake valve
opens. The downward movement of the piston draws air into the cylinder. As the
piston reaches bottom dead center, the intake valve closes, ending the intake
stroke.
(2) Compression (figure 29, view B). The piston is at bottom dead center at the
beginning of the compression stroke. The piston moves upward,
30





 Previous Page
Previous Page
