LESSON CONTENT
Part A.
1. Engine Construction. Upon completion of Part A, you will be able to
answer questions about the characteristics and principles of operation of
twostroke and fourstroke cycle spark ignition engines.
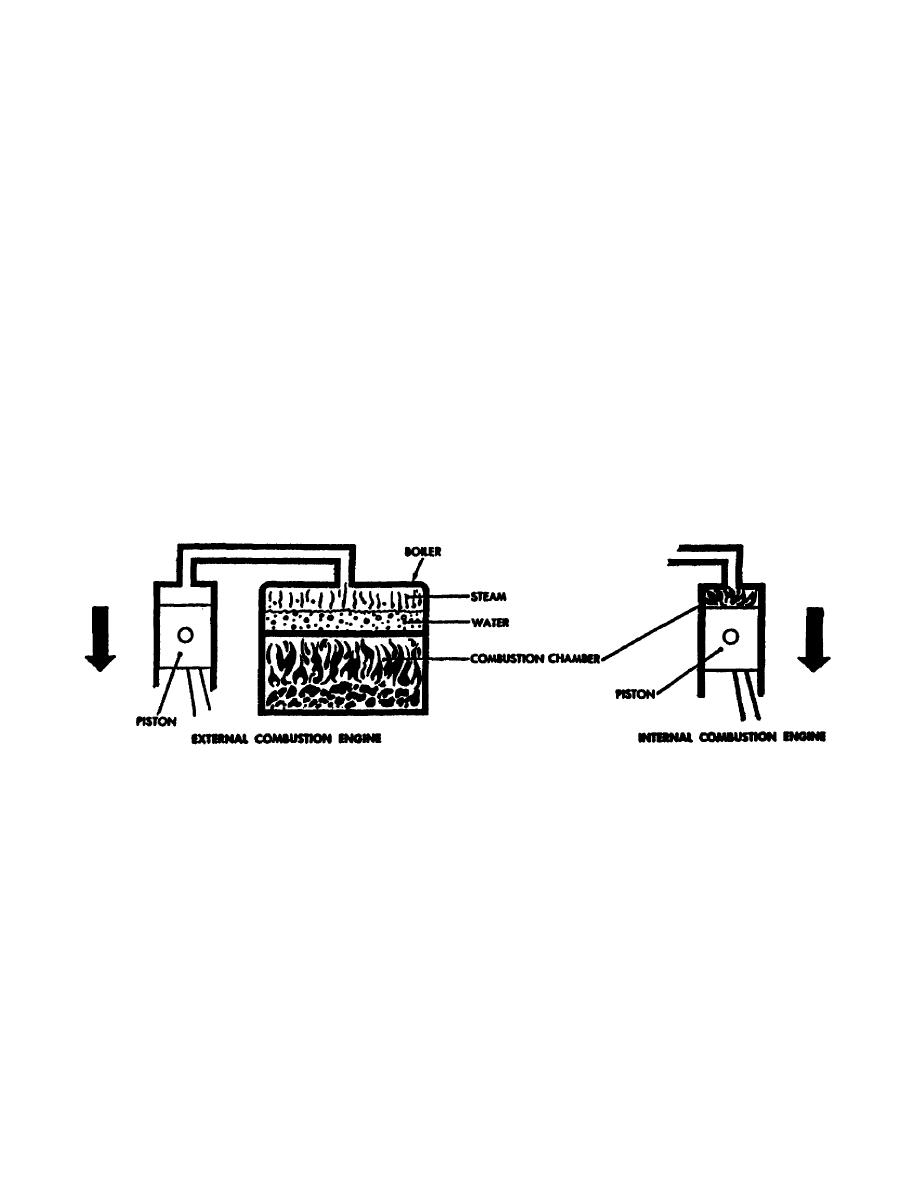
a. Internal and external combustion engines. In the internal combustion
engine, the combustion of fuel takes place inside the engine cylinder. This is
in contrast to external combustion engine, such as a steam engine, where the
combustion takes place outside. Figure 11 shows, in simplified form, an
external combustion engine. The external combustion engine requires a boiler
in which fuel is burned. This combustion causes water to boil to produce
steam. The steam passes into the engine cylinder under pressure and forces the
piston to move downward. With the internal combustion engine, the combustion
takes place inside the cylinder and is directly responsible for forcing the
piston to move downward. In both type engines, valves are arranged to permit
better intake and exhaust. The most common used engine is the internal
combustion engine.
Figure 11. Comparison of Internal and External
Combustion Engines.
3
OD0610





 Previous Page
Previous Page
