(h) Torque wrench. A torque wrench enables you to set up a nut or bolt
when the force applied to the handle reaches the specified limit. Manufacturers'
instructions specify these limits of turning force. Cylinder head nuts and bolts,
rod bearing caps, and other places on automotive and airplane engines usually
require torque wrench limits. Select proper size socket wrench and attach to
torque wrench square drive. Place socket wrench on work and pull the torque wrench
handle in the desired direction to tighten the work. The tightening torque will be
indicated on the dial or scale, depending on the type of the torque wrench used.
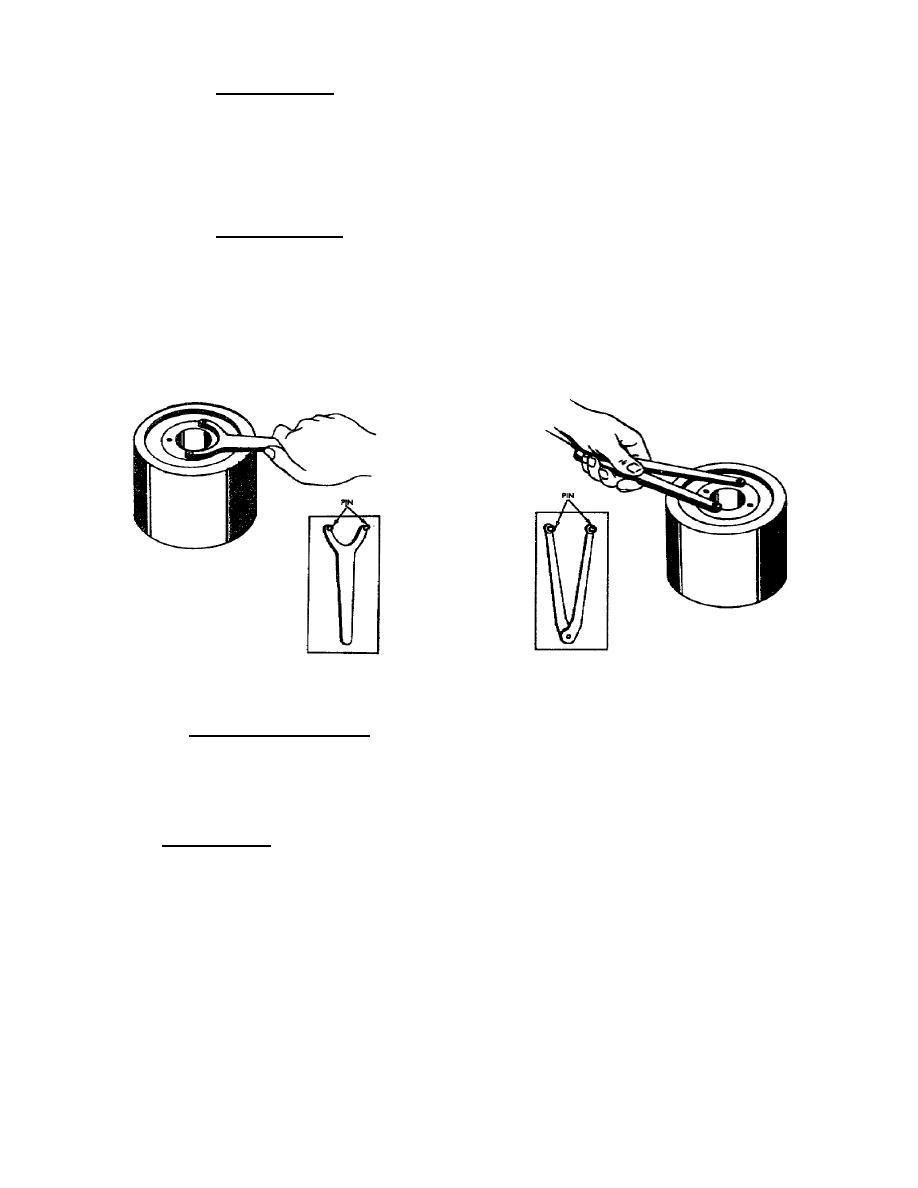
(i) Spanner wrench. When using a pin-face spanner wrench (fig 18),
insert the pins or lugs into the pinholes of the part. Keep the pin face of the
wrench flush with the part surface and turn the wrench. Exert enough force against
the wrench so that the pins do not jump out of the holes. Hose coupling spanner
wrenches are shaped so that they fit around the coupling with the pin or lug at
right angles to the handle. Insert the pin in the hose coupling pinhole. Pull or
push the handle in the direction opposite the hook of the spanner wrench. Make
certain the pin fits the hole and the force is applied with the handle
perpendicular to the work. Use of an adjustable spanner wrench is shown in figure
19.
Figure 18.
Using a pin-face spanner
Figure 19.
Using adjustable spanner
wrench.
wrench.
(2) Care and maintenance. Clean all wrenches after use. Apply a thin film
of oil to metal parts of all wrenches prior to storing. Wrenches that come in
sets, such as socket wrenches, should be returned to their cases after being used.
The torque wrench, in particular, must be carefully placed in its box to prevent
damage to the dial or scale. For long periods of storage, the wrenches should be
covered with a rust-preventive compound and carefully stored in a dry place.
d. Screwdrivers. These are used for driving or removing screws or bolts with
slotted or special heads and are made in various shapes and lengths to perform
specific jobs. The size of a screwdriver (fig 20) is indicated by the length of
the blade; i.e.; a 6-inch screwdriver has a 6-inch blade. The width and shape of
blade tips vary from a narrow parallel sided tip to a wide tapered tip. Some
screwdrivers have special tips for cross-slotted recessed screws or bolts and
clutch-bit screws. Special screwdrivers are provided with a ratchet arrangement.
15




 Previous Page
Previous Page
